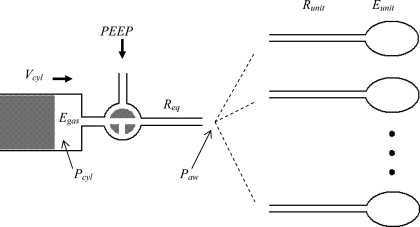
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the computational model showing a piston ventilator pushing a volume (Vcyl) that is divided into compression of the cylinder gas [determined by cylinder pressure (Pcyl) and gas elastance (Egas)] and flow into the lung through equipment resistance (Req). The airway pressure (Paw) is applied to all parallel lung units, each having resistance (Runit) and elastance (Eunit). Positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) is applied to the lung during expiration.