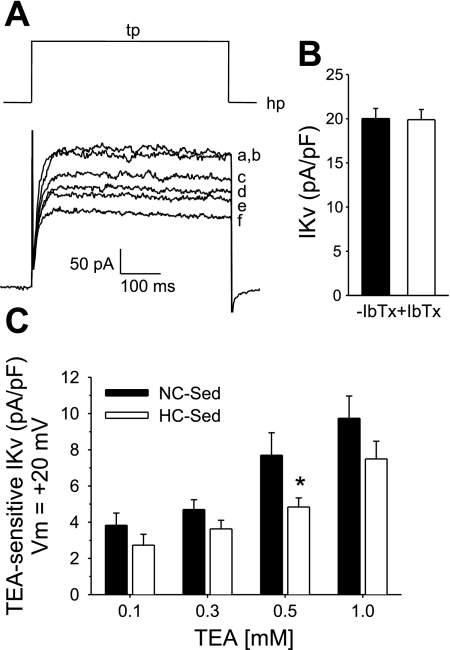
Fig. 4.
Concentration-dependent effect of the K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA) on whole cell K+ currents in coronary arteriolar smooth muscle cells. A: representative current traces from a cell of a control pig demonstrating that outward K+ current was not affected by inclusion of iberiotoxin (IbTx; 100 nM) in superfusate at step depolarizations to +20 mV (hP = −80 mV) indicating no contamination of the selective large-conductance, Ca2+-dependent K+ channel (BKCa) current in whole cell measures [control current in presence (a) and absence (b) of IbTx, respectively]. In contrast, in the presence of IbTx, TEA effectively inhibited K+ current in a concentration-dependent manner [0.1 (c), 0.3 (d), 0.5 (e), and 1 (f) mM TEA, respectively]. B: mean current data (n = 13 cells) illustrating lack of effect of IbTx on whole cell Kv currents at Vm = +20 mV. C. Mean data representing TEA-sensitive currents in cells from NC-Sed and HC-Sed pigs. Data are average of 12–26 cells from 4–6 animals. Values are means ± SE. *P ≤ 0.05 HC-Sed vs. NC-Sed.