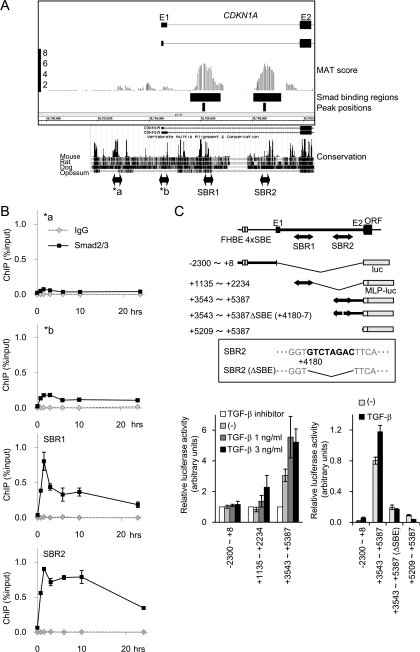
FIG. 5.
Novel Smad binding regions in the first intron of the CDKN1A gene. (A) Schematic representation of novel Smad binding regions in the CDKN1A gene. MAT scores, significant Smad2/3 binding regions, and peak positions are shown as in Fig. 1B. Interspecies conservation of genomic sequences was obtained from the University of California Santa Cruz genome browser and is shown in the lower panel. E1/E2, exons 1 and 2; a/b, positions of amplicon analyzed in panel B. (B) Validation of Smad2/3 binding to the CDKN1A intronic regions by ChIP-qPCR. HaCaT cells were treated as for Fig. 1A, and Smad2/3 ChIP samples were quantified by ChIP-qPCR, with each primer amplifying the position indicated in panel A. (C) Confirmation of TGF-β-induced transcriptional response in CDKN1A SBR1/2 by luciferase reporter assays. The upper panel shows a schematic representation of the reporter constructs used. The inset shows the identified SBE within SBR2 and its mutant used in the following experiment. (Lower left) HaCaT cells were transfected with the reporters indicated and treated with TGF-β or TGF-β type I receptor kinase inhibitor A44-03 (represented as TGF-β inhibitor, 1 μM), and luciferase activities were determined. (Lower right) HaCaT cells were transfected with the reporters indicated and treated with TGF-β, and luciferase activities were determined. MLP, minimal luciferase promoter; FHBE 4×SBE, reported forkhead transcription factor binding element and four tandem SBEs (45). Error bars represent the standard deviations.