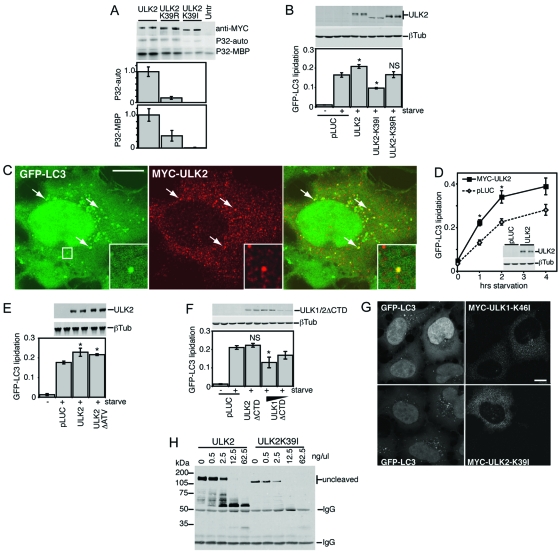
FIG. 4.
Autophagy regulatory roles of wild-type and kinase-dead ULK2. (A) In vitro autophosphorylation and MBP kinase activities for ULK2 constructs were measured as described in the legend for Fig. 1. (B, D, E, and F) Modulation of GFP-LC3 lipidation by ULK constructs was detected as described in the legend for Fig. 2. (B) *, P < 0.05; NS, P = 0.94 (in pairwise comparisons with pLUC-transfected, starved cells). (D) *, P < 0.03 in pairwise comparisons with pLUC-transfected cells at the same time point. (E) *, P < 0.06 in pairwise comparisons with pLUC-transfected, starved cells. (F) *, P < 0.02; NS, P = 0.42 (in pairwise comparisons with pLUC-transfected, starved cells). (C) In 293/GFP-LC3 cells starved in EBSS-leupeptin for 2 h, Myc-tagged ULK2 could be observed on multiple cytoplasmic structures, a portion of which colocalized with GFP-LC3, as indicated by arrows and the boxed inset. Bar = 10 μm. (G) Myc-tagged ULK1-K46I or ULK2-K39I inhibited the formation of cytoplasmic GFP-LC3-labeled autophagosomes in starved 293/GFP-LC3 cells. Bar = 10 μm. (H) Limited proteolysis of wild-type ULK2 and ULK2-K39I, assayed as described in the legend for Fig. 3. Untr, untransfected; P32-auto, ULK1 autophosphorylation; P32-MBP, MBP phosphorylation; βTub, β-tubulin; IgG, immunoglobulin G.