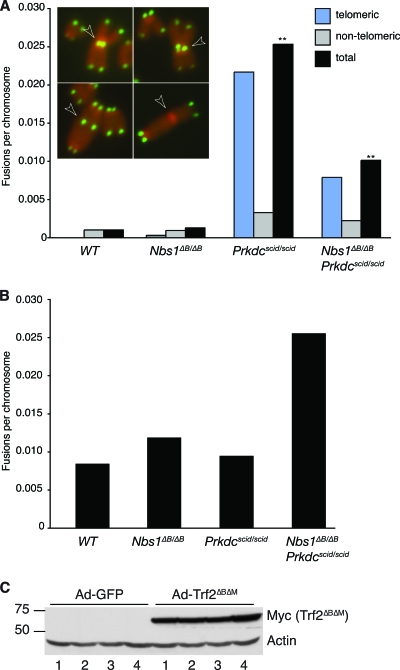
FIG. 4.
(A) Analysis of spontaneous chromosome fusions in SV40-transformed cultures of the indicated genotypes by telomere-specific FISH. Examples of chromosome fusions with telomeric sequence (top left and bottom left), a chromatid fusion involving telomeric sequence (top right), and a chromosome fusion without telomeric sequence (bottom right) are shown and are indicated by arrowheads. The total fusions per chromosome are shown and are further classified as telomeric or nontelomeric. Increased spontaneous fusions involving telomere sequence were observed in transformed Prkdcscid/scid MEFs. Increased fusions in Nbs1ΔB/ΔB Prkdcscid/scid cultures were also observed, but their frequency was significantly reduced compared to that in Prkdcscid/scid single mutants (**, P = 2.5e−9; Wilcoxon rank sum test). DAPI banding data indicating that fusions were nonclonal are presented in Table S3 in the supplemental material. (B) Telomeric fusions induced by Trf2ΔBΔM expression. Similar numbers of fusions were induced after Trf2ΔBΔM expression regardless of the genotype. Fusion numbers were normalized to those in cultures infected with Ad-GFP to account for spontaneous fusion levels. (C) Western blot analysis of the expression of Myc-tagged Trf2ΔBΔM in Ad-GFP- or Trf2ΔBΔM-expressing adenovirus (Ad-Trf2ΔBΔM)-infected MEFs. Lanes: 1, WT; 2, Nbs1ΔB/ΔB; 3, Prkdcscid/scid; and 4, Nbs1ΔB/ΔB Prkdcscid/scid. Actin was included as a control for protein loading.