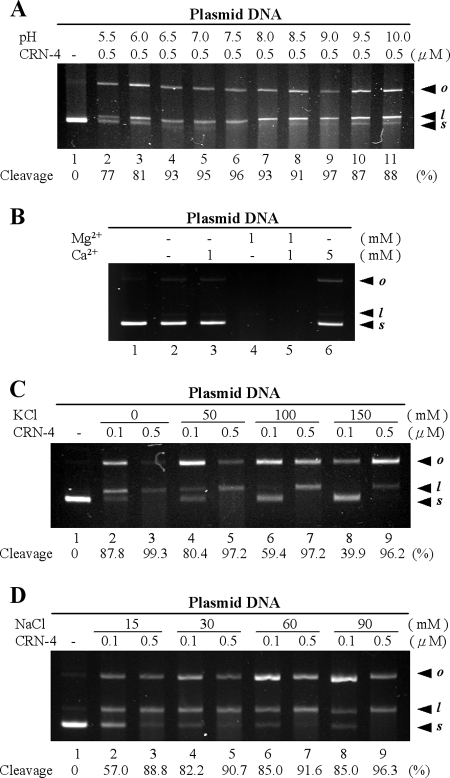
FIG. 3.
DNase activity assays of CRN-4 in different pH and salt conditions. (A) pQE30 plasmids were digested by CRN-4 in 1 mM Mg2+ and 100 mM NaCl buffered at different pH (20 mM MES at pH 5.5 and 6.0; 20 mM HEPES at pH 6.5, 7.0, and 7.5; 20 mM Tris-HCl at pH 8.0, 8.5, and 9.0; 20 mM CAPS at pH 9.5 and 10.0). The optimal pH for CRN-4 was 6.5 to 9.0. The starting supercoiled substrate (s) was cleaved by CRN-4 to generate linear DNA (l) and open-circle DNA (o). The intensity of the supercoiled substrate gel band was quantified, and the substrate cleavage percentage was estimated and is indicated at the bottom of each lane. (B) Assays of plasmid digestion by CRN-4 in the presence of Mg2+ and/or Ca2+ show that Ca2+ is a weaker cofactor of CRN-4 (lanes 3 and 6) than Mg2+ (lane 4), suggesting that CRN-4 is a Mg2+-dependent enzyme. (C) Plasmid digestion by CRN-4 in the presence of various concentrations of K+. The supercoiled substrate cleavage percentages are indicated below the gel. (D) The DNase activity of CRN-4 increased as the Na+ concentration increased from 15 to 90 mM.