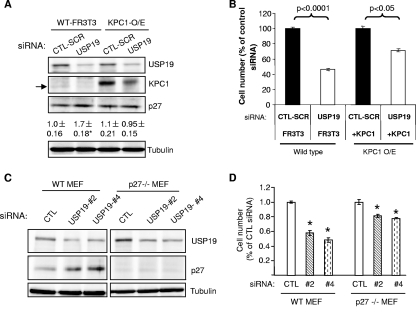
FIG. 6.
USP19 modulates cell growth through KPC1/p27Kip1-dependent and -independent pathways. (A, B) KPC1 overexpression normalizes p27Kip1 levels and partially rescues growth defects of USP19-depleted cells. Wild-type (WT) or FR3T3 cells stably overexpressing (O/E) KPC1 were transfected with USP19 siRNA or scrambled control oligonucleotide (CTL-SCR). After 48 h, the cells were counted or harvested in a denaturing buffer. (A) Proteins from cells exposed to the indicated siRNA oligonucleotides were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (arrow indicates endogenous KPC1, which migrates faster than overexpressed epitope-tagged KPC1). Shown below the p27Kip1 blot is quantitation of p27Kip1 protein as means ± standard errors. *, P value of <0.025 compared to result for CTL-SCR. (B) Cell numbers in the different treatment groups. Shown are means ± standard errors. (C, D) Ability of USP19 depletion to inhibit cell growth is partially blocked in MEF lacking p27Kip1. Wild-type or p27Kip1−/− MEF were transfected with USP19 siRNA (#2, no. 2; #4, no. 4) or nonspecific control oligonucleotide (CTL). After 48 h, the cells were counted or harvested in a denaturing buffer. (C) Proteins from cells exposed to the indicated siRNA oligonucleotides were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) Cell numbers in the different treatment groups. Shown are means ± standard errors. *, P value of <0.001 compared to result for CTL.