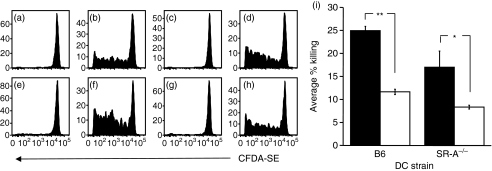
Figure 6.
Scavenger receptor A (SR-A)−/− bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) are efficient in the uptake of glycoprotein 96 (gp96) and the processing and presentation of gp96-bound peptides to CD8+ T cells (TCD8+). 5-(and 6-)carboxyfluorescein diacetate–succinimidyl ester (CFDA-SE)-labelled OT-1.SJL splenocytes were adoptively transferred into naïve recipient mice. Wild-type (a–d) and SR-A−/− (e–h) BMDCs were pulsed with 10 μg of gp96 (a, c, e, g) or gp96 ovalbumin (OVA)257–264 (b, d, f, h) at 4° (a, b, e, f) or 37° (c, d, g, h) for 30 min and transferred intravenously into recipient wild-type mice. Proliferation of adoptively transferred OT-1.SJL TCD8+ was determined via CFDA-SE dye dilution 72 hr post immunization. The proportion of adoptively transferred cells proliferating was not significantly different (P > 0·05) between panels (b) and (f), or (d) and (h). Mice were immunized with wild-type or SR-A−/− BMDCs pulsed with gp96-OVA257–264 (i) in the absence (closed bars) or presence (open bars) of fucoidin. Seven days post immunization, CFDA-SE-labelled B6.SJL targets pulsed with relevant or irrelevant peptide were adoptively transferred into wild-type or SR-A−/− mice. Effector function was measured as the percentage of targets killed. **P < 0·05; *P < 0·06; NS, not significant (P > 0·05).