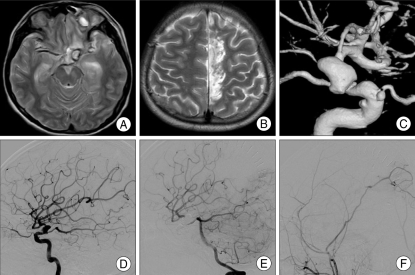
Fig. 2.
Patient 14. Magnetic resonance (MRI) showing a small mass lesion with hemorrhage at the left frontal base (A). Three months after the injury, the patient complained of right leg weakness; MRI shows a new infarction of the left distal anterior cerebral artery territory (B). A 3D angiogram showing a traumatic pseudoaneurysm at the left ICA dorsal wall and multiple aneurysms at the left ophthalmic artery and cavernous in the internal cerebral artery (ICA) (C). Angiograms demonstrating dorsal wall aneurysm before surgery (D), after superficial temporal artery-middle cerebral artery (STA-MCA) bypass surgery (E), and after ICA occlusion with a coil (F). Distal MCA flow is observed to fill via the posterior communicating artery and anastomotic vessel.