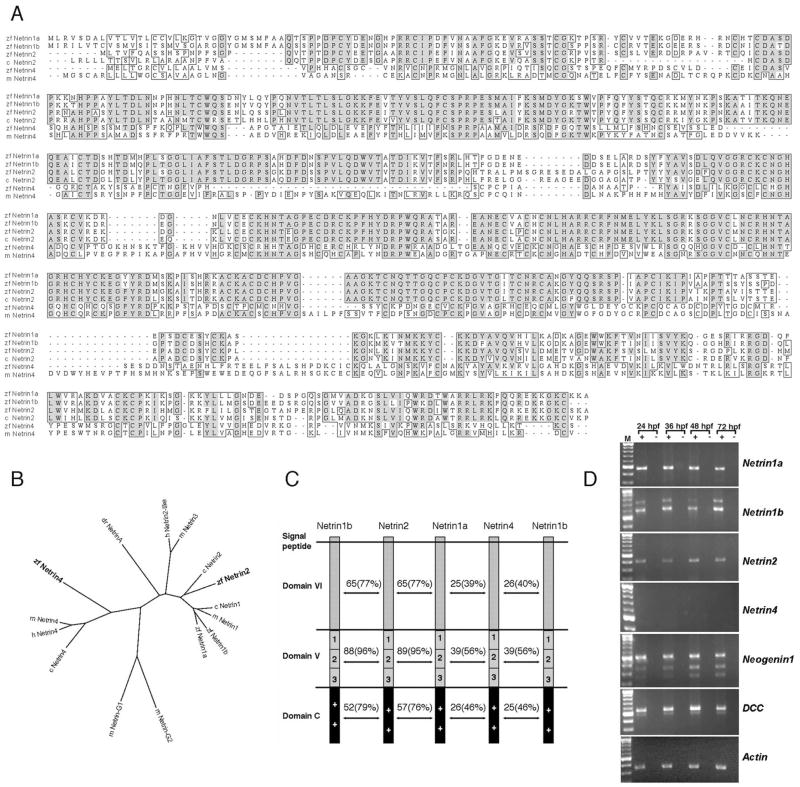
Fig. 1.
ClustalW amino acid alignment of Netrin sequences and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) expression analysis of Netrin and Netrin receptor genes. A: Alignment of chick Netrin2 and mouse Netrin4 with zebrafish Netrin2 and Netrin4. Dark and pale gray boxes represent, respectively, identical and similar amino acids. zf, zebrafish; m, mouse; c, chick. B: Phylogenetic analysis of predicted zebrafish Netrin proteins based on ClustalW alignment using the Biology Workbench site (http://workbench.sdsc.edu). zf, zebrafish; h, human; m, mouse; c, chick; dr, Drosophila. Zebrafish Netrin2 is most closely related to chick Netrin2, whereas zebrafish Netrin4 is closely related to human and mouse Netrin4. The GPI-linked proteins Netrin-G1 and -G2 are included for comparison. C: Zebrafish Netrin2 and Netrin4 contain all the domains (domains VI, V, and C) described in other Netrin family members. Numbers indicate identity, and parentheses represent similarities between two given proteins. Netrin2 is highly similar to Netrin1a and 1b, while Netrin4 is the most divergent member of the Netrin family. D: RT-PCR analyses were performed to detect netrin transcripts in total RNA collected from 24, 36, 48, and 72 hpf embryos. Actin amplification served as a loading control, and mock amplifications (−, no RT) confirmed that bands represent amplification of RNA. Netrin2 is expressed from 24 hpf through 72 hpf, whereas netrin4 is not detected at any of these stages (25 cycles). Netrin1a, netrin1b, dcc, and neogenin1 are expressed at all stages.