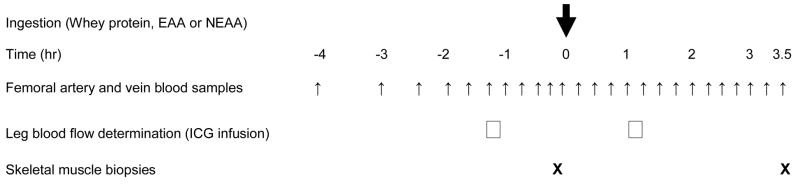
Fig. 1.
Diagram of the blood and muscle sampling protocol. Data were collected before and after ingestion (at time 0) of 15 g of whey protein, 6.72 g of essential amino acids (EAA), or 7.57 g of non-essential amino acids (NEAA). The EAA and NEAA mixtures contain the EAA and NEAA, respectively, found in the 15 g of the whey protein. Leg arterio-venous blood samples were taken at several times before and every 15 minutes following the ingestion of either whey protein or amino acid mixtures for the determination of the leg blood phenylalanine balance. Blood flow was determined before and following ingestion of the three mixtures and by using indocyanine green (ICG) dye infusion in the femoral artery. A leg muscle biopsy was performed at the end of the sampling protocol to determine changes in the muscle free phenylalanine concentration compared to the period prior to the ingestion of the whey protein or amino acids mixtures.