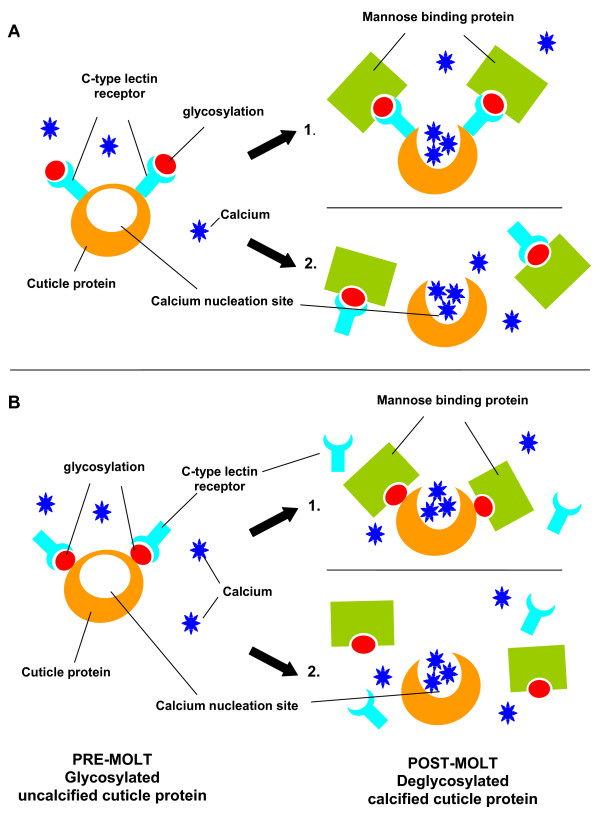
Figure 2.
Alternative conceptual models depicting the proposed involvement of C-type lectin receptors and mannose binding protein in the regulation of calcification. A C-type lectin receptors bind to the cuticle protein thus facilitating glycosylation. Mannose binding protein binds to glycosylated regions thereby exposing the calcium nucleation site and enabling calcification, by either conformational change (A1) or deglycosylation (A2). B C-type lectin receptor binds to the sugar moieties of the glycosylated cuticle proteins, masking the calcification nucleation site. Competitive binding by the mannose binding protein to the glycosylation sites facilitates calcification exposing the calcium nucleation site either through conformational change to the cuticle protein (B1) or by deglycosylation (B2).