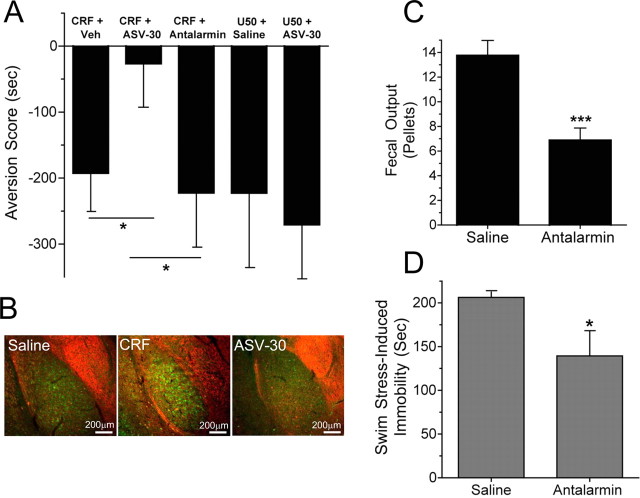
Figure 6.
CRF2-R antagonism blocks CRF-induced, but not U50,488-induced, aversion. A, CRF-induced place aversion was blocked by ASV-30 (1 nmol, i.c.v.) pretreatment, whereas antalarmin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) pretreatment did not. U50,488 also induced a place aversion, and ASV-30 pretreatment did not block this aversion. Veh, Vehicle (see Materials and Methods). *p < 0.05, significantly different from ASV-30 (n = 10–11 animals per group). B, Representative images showing that the increase in KORp-ir (green) in the basolateral amygdala caused by CRF injection (middle panel) compared with saline (left panel) was blocked by pretreatment with ASV-30 (right panel). Counterstained for GAD67-ir (red). C, Injection of the CRF1-R-selective antagonist antalarmin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) before swim-stress testing significantly blocked stress-induced colonic motility (fecal output) (n = 8; ***p < 0.001; t test) as reported previously (Griebel et al., 2002). D, Injection with antalarmin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly blocked swim stress-induced immobility (n = 4; *p < 0.05; t test), demonstrating that this dose of antalarmin was pharmacologically active.