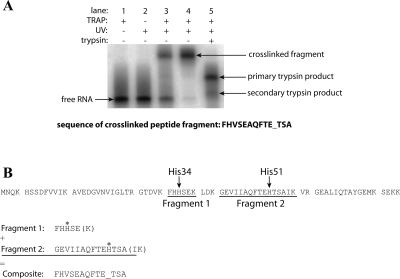
FIGURE 3.
Photochemical cross-linking of U21 5IU-substituted RNA. (A) Denaturing PAGE separation of cross-linked macromolecules. (Lane 1) U21 5IU-substituted RNA incubated with T30V TRAP; (lane 2) U21 5IU-substituted RNA exposed to UV light; (lane 3) U21 5IU-substituted RNA incubated with T30V TRAP and exposed to UV light; (lane 4) purified cross-linked protein–RNA complex; (lane 5) partial trypsin digest of the purified cross-linked fragment. As TRAP is highly stable, trypsin digests of the purified cross-linked fragment under standard reaction conditions yielded incomplete cleavage of the peptide fragment (lane 5, primary trypsin product band). When the reaction was conducted under more denaturing conditions (see Materials and Methods; data not shown), the secondary trypsin product became the predominant species (lane 5, secondary trypsin product band). This secondary trypsin product fragment was used in the N-terminal sequencing reaction. The resulting sequence of the cross-linked peptide fragment is shown below the gel. Amino acids involved in chemical cross-links appear as blank cycles (underscored) during the sequencing reaction because the large RNA molecule covalently attached to the side chain interferes with the sequencing analysis. (B) Alignment of the cross-linked peptide fragment(s) with TRAP. The sequence of TRAP is shown broken into tryptic fragments. The results indicate that instead of cross-linking to a single residue, the photoactive nucleobase reacted with two separate amino acids (asterisks). These residues are His34 in Fragment 1 and His51 in Fragment 2. As the N-terminal sequencing reaction is indiscriminant, the instrument defaulted to amino acids in the more abundant fragment (Fragment 1) at a given position. When one of these amino acids was cross-linked (His34), the residue from the less abundant fragment (Fragment 2) was detected instead (Val43). When the end of the shorter fragment (Fragment 1) was reached, the instrument detected amino acids from the less abundant but longer fragment (Fragment 2). The cross-linked amino acid in this region (His51) appeared as a blank cycle. The C-terminal amino acids (shown in parentheses) of each fragment were not detected in the sequencing reaction.