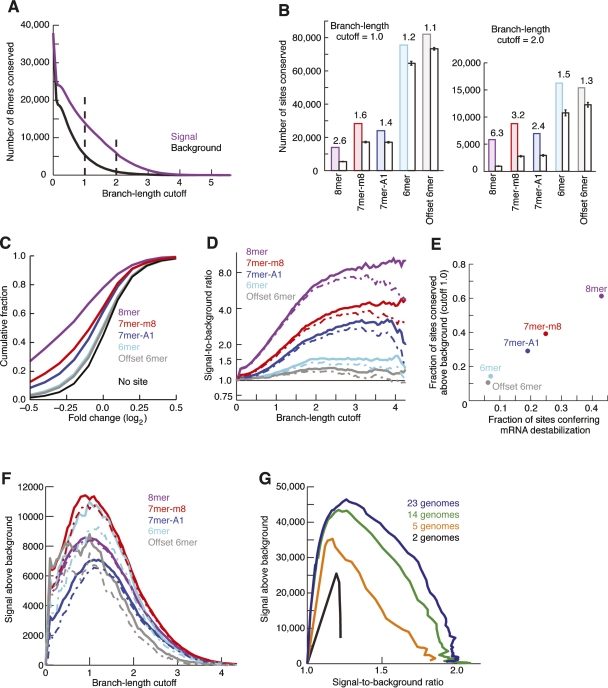
Figure 2.
Conservation of major seed-match types. (A) Conservation of 8mer sites for 87 broadly conserved miRNA families. High-sensitivity and high-specificity cutoffs are highlighted with broken lines at 1.0 and 2.0, respectively. (B) Conservation and background estimate for mutually exclusive site types at high sensitivity (left) and high specificity (right). The signal-to-background ratio is indicated above the pair of bars. Error bars indicate one standard deviation in the estimated background, based on subsampling of individual control k-mers. (C) Efficacy of offset 6mer sites. Microarray data monitoring mRNA destabilization following transfection of 11 miRNAs was analyzed as described previously (Grimson et al. 2007). Shown is the cumulative distribution of changes for transcripts containing exactly one offset 6mer site and no other canonical sites in their 3′UTR. For comparison, previously reported analyses of messages with single canonical sites are also shown (Grimson et al. 2007). (D) Signal-to-background ratio for indicated sites at increasing branch-length cutoff. Broken lines indicate 5% lower confidence limit (z-test). (E) Correlation of site conservation rate and experimental efficacy. Fraction of sites conserved above background was calculated as ([Signal – Background]/Signal) at a branch-length cutoff of 1.0. The minimal fraction of sites conferring destabilization was determined from the cumulative distributions (C), considering the maximal vertical displacement from the no-site distribution (correcting for the bumpiness of the distributions as described previously [Grimson et al. 2007]). (F) Estimates of signal above background for the major site types. Broken lines indicate 5% lower confidence limit (z-test). (G) Aggregate conservation above background for all major site types when using using subsets of genomes. To facilitate overlay of the plots, the X-axis is signal-to-background ratio rather than branch-length cutoff. The 14-genome subset represents the non-fish species originally available in the UCSC 17-way alignments. The five-genome subset contains human, mouse, rat, dog, and chicken, and the two-genome subset contains only human and mouse.