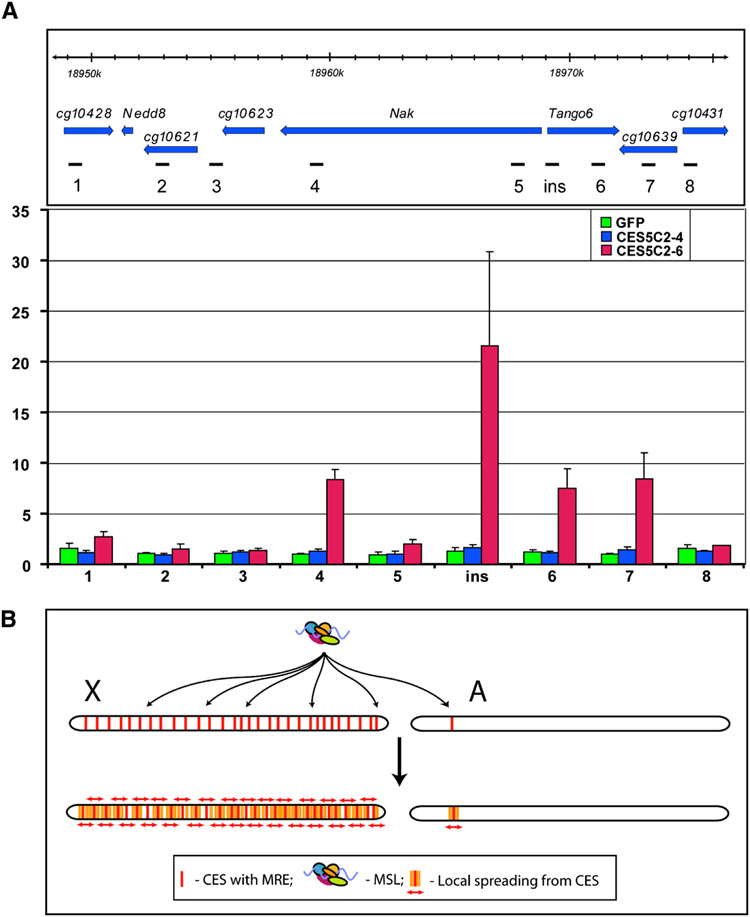
Figure 7. MSL complex spreads into neighboring genes from CES5C2 inserted on an autosome.
(A) MSL3-TAP ChIP in the region surrounding the 37B7 integration site where either GFP (1.9 kb), CES5C2-4 (258 bp, no MREs) or CES5C2-6 (268 bp, three MREs) are placed (y w; CES-X{37B7}/ MSL3-TAP; H83M2-6I, msl3 mixed sex embryos). Top panel: genetic map and location of probes, Dm3 release coordinates are shown. Bottom panel: MSL3-TAP data for GFP (green), CES5C2-4 (blue) and CES5C2-6 (red), indicate that only CES5C2-6 effectively targets the MSL complex and directs limited spreading to neighboring genes. (B) Two-step model for MSL targeting of the X chromosome. X, X chromosome, A, autosome. First step: MSL complex targets >150 chromatin entry sites containing MRE motifs on the X chromosome. The autosome is normally ignored, unless a CES from the X is inserted on the autosome. Second step: Local spreading from entry sites leads to MSL binding to the majority of active genes on the X chromosome. In addition, an ectopic CES can lead to targeting of flanking active genes on an autosome, as seen in the results displayed in panel A.