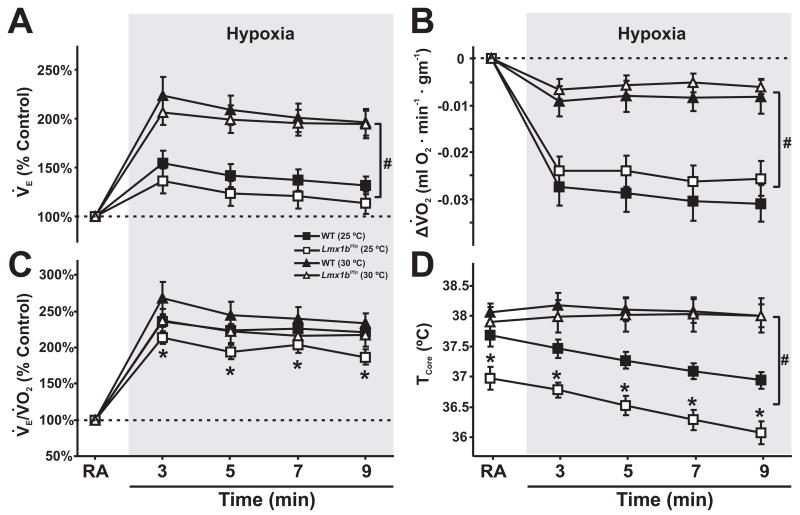
Figure 4. The ventilation to oxygen consumption ratio is reduced at 25°C due to a reduced body temperature in Lmx1bf/f/p mice.
A, Minute ventilation (VE; % control), B, V̇O2, C, V̇E/VO2 ratio (% control), and D, core temperature (TCore) in WT (solid symbols) and Lmx1bf/f/p (open symbols) mice at TAmb of 25°C (squares) and 30°C (triangles (Hodges, M. R. et al., 2008b)). Note that both genotypes shift ventilatory and metabolic strategies during hypoxia at different TAmb, and that the V̇E/VO2 ratio is reduced under cool conditions. Two-way ANOVA (genotype and time, or TAmb as factors) and unpaired t-test, * denotes P<0.05 for WT versus Lmx1bf/f/p mice, # denotes P<0.05 for 25°C versus 30°C. Data are mean ± SEM.