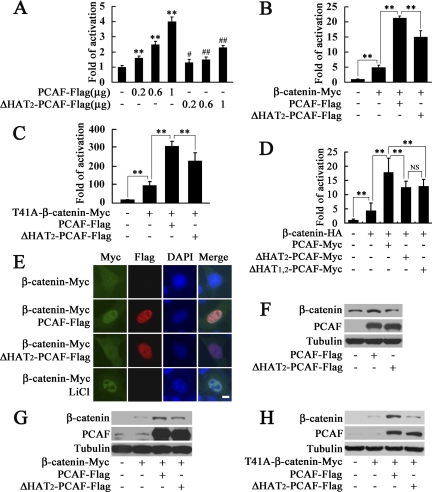
Figure 1.
PCAF enhances β-catenin transcriptional activity, induces its nuclear translocation and up-regulates its protein level. (A) PCAF activated β-catenin transcriptional activity in a dose-dependent manner. HEK293T cells were transfected with Super8×TOPFlash and the indicated amount of PCAF-FLAG or ΔHAT2-PCAF-FLAG for luciferase assay. **p < 0.01, versus the cells transfected with empty vector; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, versus the cells transfected with equal amount of PCAF-FLAG. In this and all other figures, error bars represent SD (B–D) PCAF synergized with β-catenin or T41A-β-catenin to activate Super8×TOPFlash. **p < 0.01; NS, no significant difference. (E) PCAF induced nuclear translocation of β-catenin. HeLa cells were transfected with indicated constructs. After transfection for 28 h, the cells shown (bottom) were treated with 20 mM LiCl. After transfection for 40 h, cells were fixed and immunostained with anti-Myc or anti-FLAG antibody. Nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining. Bar, 10 μm. (F) Up-regulation of endogenous β-catenin by increased expression of PCAF. After transfection with PCAF-FLAG or ΔHAT2-PCAF-FLAG in HEK293T cells for 40 h, total β-catenin, PCAF, and tubulin level in the extract were detected by Western blot. (G and H) PCAF increased β-catenin protein level when cotransfected with β-catenin-Myc or T41A-β-catenin-Myc. After transfection with indicated constructs in HEK293T cells for 40 h, β-catenin, PCAF, and tubulin in cell lysates were detected with anti-Myc, anti-PCAF, or anti-tubulin antibody.