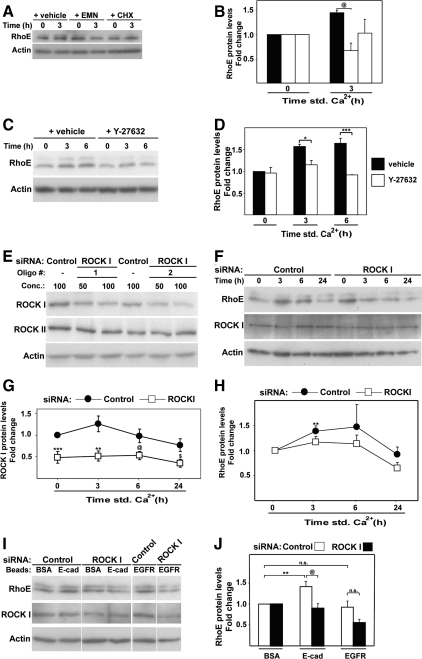
Figure 2.
Increase in RhoE protein levels requires ROCKI function. Keratinocytes grown in low calcium medium were treated as described below and induced to differentiate by adding calcium ions to the medium (A–H) or left in low calcium medium (I and J). Equal amount of protein was probed with antibodies against the indicated proteins. (A) Inhibition of protein synthesis by cycloheximide (CHX) or emetine (EMN) prevents differentiation-specific RhoE up-regulation. Keratinocytes were pre-incubated with inhibitors and induced to differentiate for 3 h in the presence of each inhibitor. (B) Quantification of the results shown in A. (C) Keratinocytes were incubated in the presence or absence of Y27632 to inhibit ROCK kinase activity. (D) Quantification of results from C. (E) ROCKI siRNA optimization using two different siRNA oligos against ROCKI or nontargeting control. (F) Time course of keratinocyte differentiation after treatment with control or ROCKI siRNA oligos. (G) Protein levels for ROCKI were quantified and expressed relative to control time zero. (H) RhoE protein levels were quantified and normalized for time zero of each group (control or ROCKI RNAi). (I) siRNA-treated keratinocytes (nontargeting control or ROCKI) were exposed for 1 h in low calcium medium to beads coated with BSA (control) or antibodies against E-cadherin or EGFR. (J) Quantification of results from I. RhoE levels found in cells treated with control BSA-beads were arbitrarily set as 1. Error bars represent SE. N = 3 experiments, apart from panels H, J (N = 4) and G (N = 5); ***p < 0.006, **p < 0.009, *p < 0.02, @p < 0.04, and $p < 0.05.