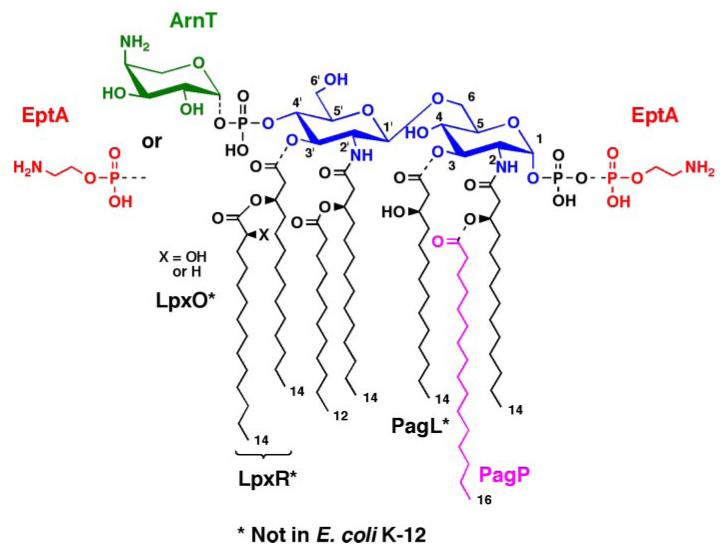
FIGURE 1. Regulated covalent modifications of lipid A in E. coli and S. typhimurium.
As indicated by the dashed bonds, modifications of the phosphate groups and/or acyl chains of lipid A are observed under certain growth conditions or in some mutants (2). The phosphates can be modified with L-Ara4N and/or pEtN groups, both of which are regulated by pmrA (26). The latter gene, encoding the PmrA transcription factor (73), is constitutively active in polymyxin-resistant mutants, and the relevant modifying enzymes ArnT (31) and EptA (22, 23) are induced under these conditions. In some instances, lipid A species are made in which the locations of the L-Ara4N and pEtN groups are reversed (20, 88), or in which both phosphates are modified with the same group, as is the case with pEtN when L-Ara4N synthesis is blocked (21). The outer membrane enzyme PagP (89) can add an additional palmitate unit at position 2, whereas PagL (90) can remove the hydroxymyristoyl chain at position 3. These pag genes are regulated by the PhoP/PhoQ system (91), which can be activated by low Mg2+ in Salmonella. PagL (90), LpxO (92), and LpxR (93) are present in Salmonella but not E. coli K-12. However, they can function in E. coli K-12 when expressed from plasmids.