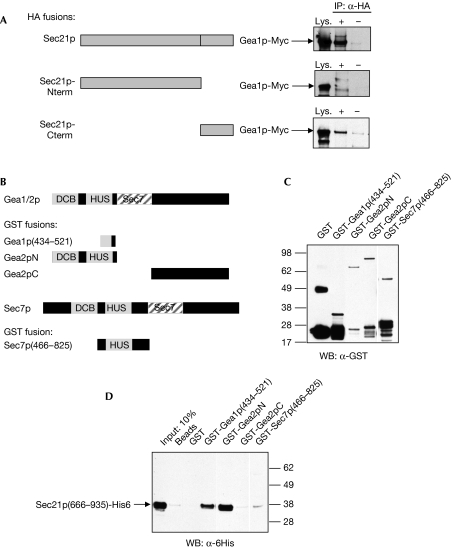
Figure 2.
Gea1p interacts with the carboxy-terminal appendage domain of Sec21p. (A) Cell lysates were prepared from strain CJY110 GEA1∷13xMyc carrying plasmids expressing the indicated portions of Sec21p-HA (Sec21p-Nterm: aa 1–665; Sec21p-Cterm: aa 666–953), and immunoprecipitations (IP) were carried out with HA antibody (+) or IgG alone (−). Western blot (WB) analysis was performed using Myc antibody to detect endogenous Myc-tagged Gea1p. (B) Schematic diagram showing regions of Gea1p, Gea2p and Sec7p expressed as GST fusions in Escherichia coli. (C) Western blot analysis of GST fusion constructs expressed in E. coli. (D) The indicated GST fusion constructs were expressed in E. coli, purified on a glutathione-Sepharose column, and Sec21p(666–935)-His6 purified from E. coli was passed over the columns. Eluates were subject to western blot analysis with His6 antibodies. The first lane shows 10% of the input of Sec21p(666–935)-His6. DCB, dimerization and cycophilin-binding domain; Gea, guanine exchange factor on Arf; GST, glutathione S-transferase; HA, haemagglutinin; HUS, homology upstream from Sec7 domain.