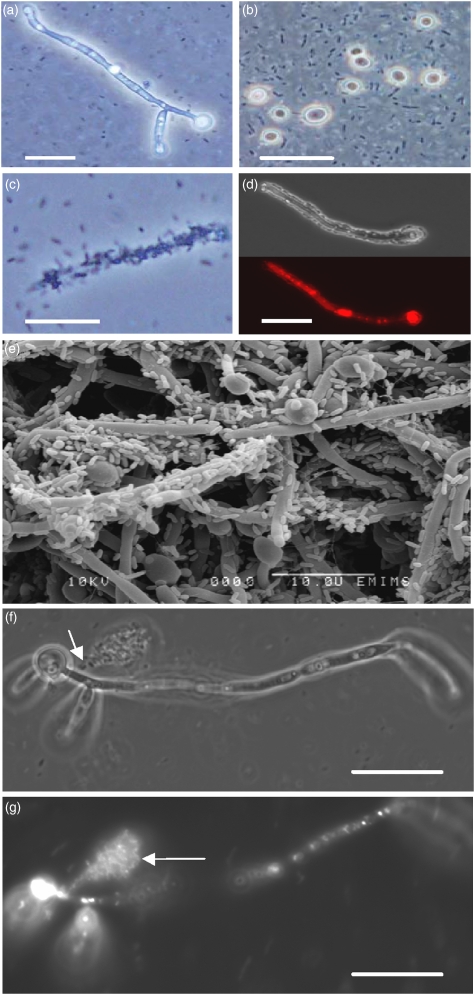
Fig. 3.
Candida albicans hyphae – adhesion, colonization and lysis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adhered hyphae were viewed by light microscopy after 3 h coincubation with P. aeruginosa in RPMI-1640. Most hyphae and all yeast cells (b) had no observable adherent bacteria (a, b); yet some hyphae were completely colonized by P. aeruginosa (c, d). After 48 h, yeast cells and some hyphae were not colonized by P. aeruginosa (e). Treatment after colonization with FUN1 LIVE/DEAD red vacuolar stain revealed that hyphae were alive before adhesion by bacteria (d). Cytosol appeared to be released from points on the hyphal surface (arrow, f). The exudate released into the medium (arrow, g) from the point of lysis was confirmed as cytosolic material by FUN1 staining. Scale bar=10 μm.