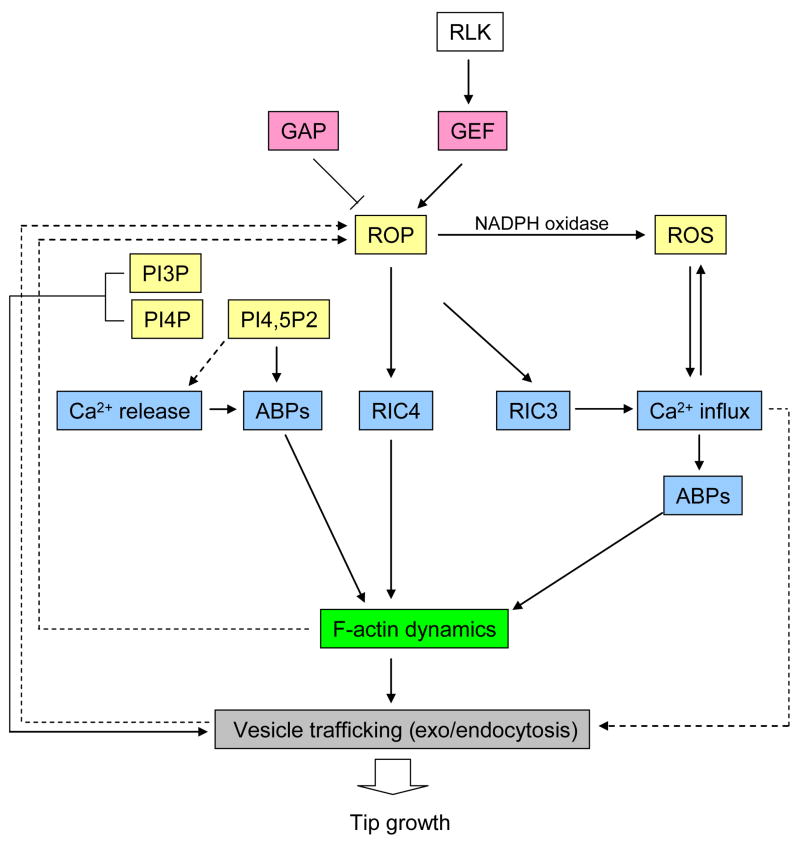
Figure 2. Signaling pathways regulating tip growth.
The available data indicate that multiple pathways are converged in F-actin dynamics, which is critical for tip growth. ROP activity has been shown to oscillate at the tip, suggesting a self-organizing mechanism involving feedback loops underlies the regulation of the apical ROP activity. ROP downstream events, such as vesicle trafficking, calcium signaling, and F-actin dynamics, are most likely to contribute to the feedback regulation of ROP activity. Phsopholipids signaling was proposed to act downstream of ROP signaling, but no direct evidence is available. Actin binding proteins (ABPs) represented here is including ADF, profilin, and villin/gelsolin/fragmin superfamily proteins, whose activities are regulated by Ca2+ and/or PIP2. Ins(1,4,5)P3-induced-Ca2+ release was observed in pollen tubes, but IP3-sensitive calcium channel has not been identified. Solid arrows represent pathways that supported by experimental data, whereas dotted arrows represent more hypothetical pathways.