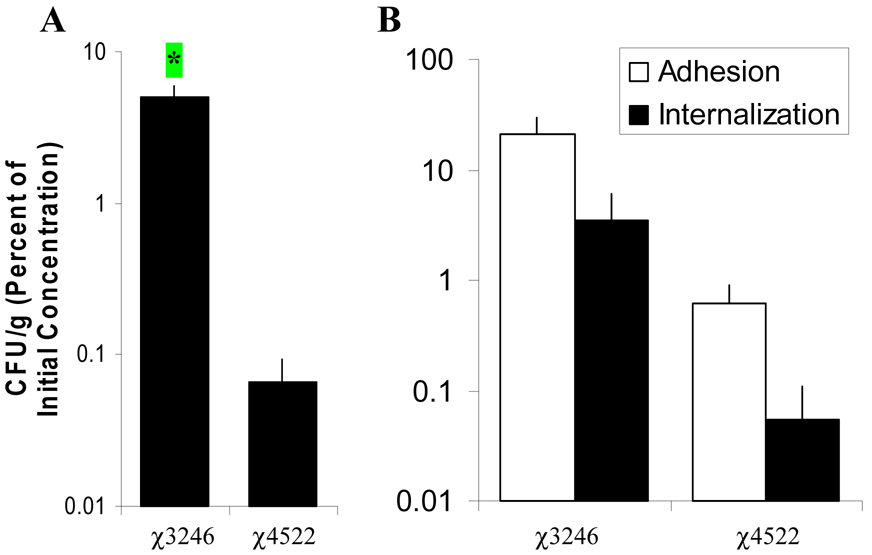
Figure 3.
Virulent Salmonella serovar Choleraesuis strain χ3246 is internalized by JPP more efficiently than attenuated strain χ4522 after exposure 2 h ex vivo. A. Tissues were exposed on their luminal aspect to 7.3 ± 0.1 log10 CFU/ml (mean ± SE) of strain χ3246 (21 JPP/10 pigs) or strain χ4522 (11 JPP/ 7 pigs) for 2 h. * p < 0.05. Commensal bacteria were detected in 9 of 31 Salmonella -infected JPP from 10 pigs, with a mean of 3.1 ± 0.5 log10 CFU/g (mean ± SE). B. Salmonella serovar Choleraesuis strain χ4522 adheres to and is internalized poorly by JPP tissue. Tissues were exposed on their luminal aspect to 6.7 ± 0.1 log10 CFU/ml (mean ± SE) of strain χ3246 or strain χ4522, both grown overnight in LB (3 JPP/3 pigs) for 2 h. Values are CFU/g tissue after 2 h, expressed as a percentage of the Salmonella inoculum in the luminal bathing medium at time zero, and the error bars show standard error. The open bar (□) represents adherent bacteria and the solid bar (■) represents internalized Salmonella.