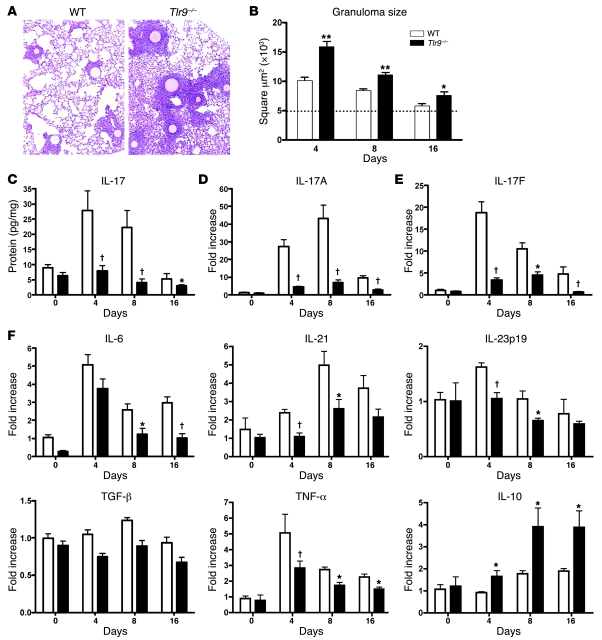
Figure 1. Tlr9–/– mice showed larger pulmonary granulomas and impaired Th17 cytokine levels.
All panels compare parameters between WT and Tlr9–/– mice. (A) Lung tissues were histologically analyzed by H&E at day 4 after initiation of lung granuloma. Original magnification, ×100. (B) Kinetic analysis of the development of lung granulomas using morphometric analysis of the evolving lung lesions in WT and Tlr9–/– mice. Dotted line represents mean granuloma cross-sectional area (μm2) ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001. (C) Protein levels of IL-17 measured in whole lungs using a Luminex system. Data shown are mean ± SEM and are from a representative experiment of 4 independent experiments. †P < 0.01. (D–F) Quantitative real-time PCR (TaqMan) was performed to measure the transcript levels of IL-17A (D), IL-17F (E), IL-6, IL-21, IL-23p19, TGF-β, TNF-α, and IL-10 (F) in whole lungs. Data shown are mean ± SEM and are from a representative experiment of 4 independent experiments. Each time point indicates at least 4–6 mice per group.