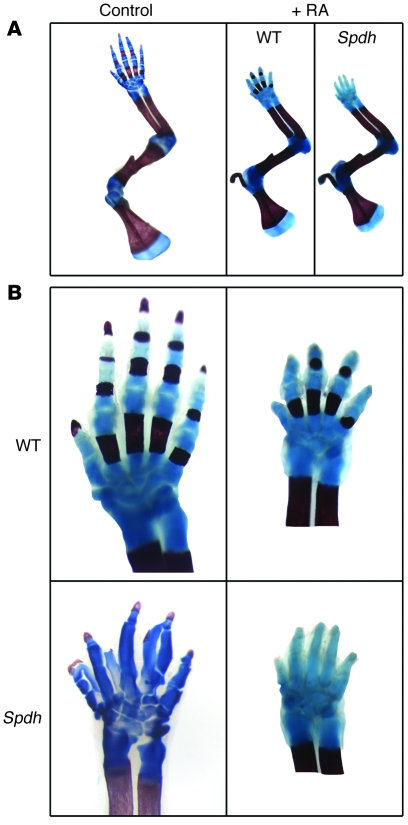
Figure 5. RA treatment rescues the polydactyly phenotype.
(A) Newborn animals were analyzed with skeletal preparations. WT littermates served as controls. Bone was stained in red, cartilage in blue. RA led to an overall reduction in bone size both in WT and Spdh compared with an untreated control. Size reduction was comparable in WT and Spdh/Spdh mice. (B) Comparison of the autopod of untreated controls (left) with RA-treated animals (right) demonstrated an overall reduction in size but normal formation of digits, cartilage, and bone in WT animals. Treated Spdh/Spdh offspring had 5 digits, demonstrating a partial rescue of the Spdh phenotype.