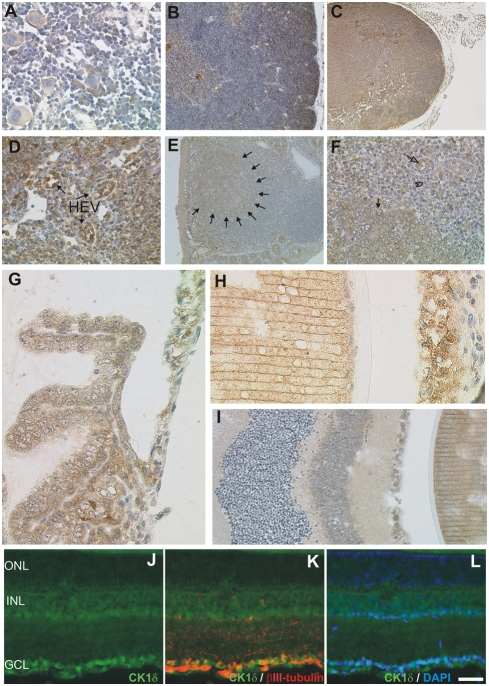
Figure 6. Localisation of CK1δ in hematopoetic and lymphoid organs and the eye.
Fixative: acid formalin, fixation by immersion. Peroxidase reaction, dye: DAB. The CK1δ specific antibody NC10 was used to detect CK1δ in hematopoetic and lymphoid organs and in the eye. (A) bone marrow; (B) thymus; (C, D) lymph node; (E, F) cecal lymphoid follicle; (G) the eye ciliary body and iris; (H) lens and iris; (I) retina and lens. Immunohistochemical analysis of frozen retinal sections reveals localisation of CK1δ in retinal ganglion cells, which were specifically co-stained with an anti-βIII-tubulin antibody or DAPI (J–L). Magnification: 100× (B, C, E), 200× (D, F), 400× (A, G–L). ONL: outer nuclear layer; INL inner nuclear layer; GCL: retinal ganglion cell layer. Scale bar: 50 µm. Arrows in D indicate high endothelial venules (HEV), arrows in E delineate a B-follicle. In F closed arrows point to a lymphoid blast, the arrowhead points to a small resting lymphocyte and the open arrow indicates high endothelial venule.