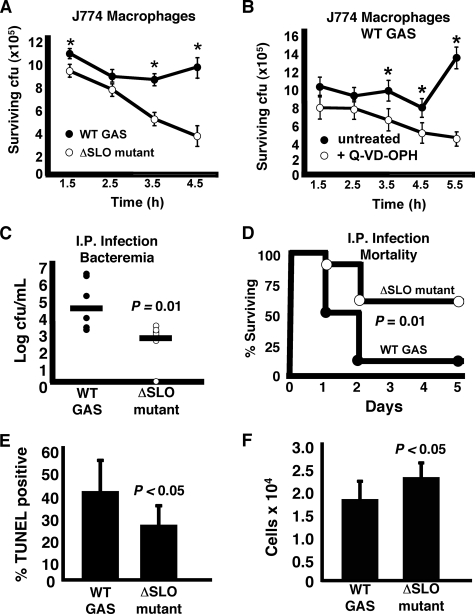
FIGURE 9.
SLO induction of macrophage apoptosis enhances bacterial survival and promotes virulence in vivo. A, higher survival of WT GAS versus ΔSLO mutant in the presence of macrophages. Experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times. B, caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPH enhances the ability of macrophages to kill WT GAS. Experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times. * = p < 0.05. C, higher numbers of WT GAS than ΔSLO mutant recovered from blood of mice injected intraperitoneally (I.P.). t = 24 h. D, ΔSLO mutant is significantly attenuated (60% survival) versus the WT GAS (10% survival) in a mouse systemic infection model. E, higher level of apoptosis was detected in the peritoneal cells of mice infected with GAS WT compared with the ΔSLO mutant. F, fewer peritoneal cells were collected from mice infected with WT GAS, demonstrating SLO-mediated immune cell depletion.