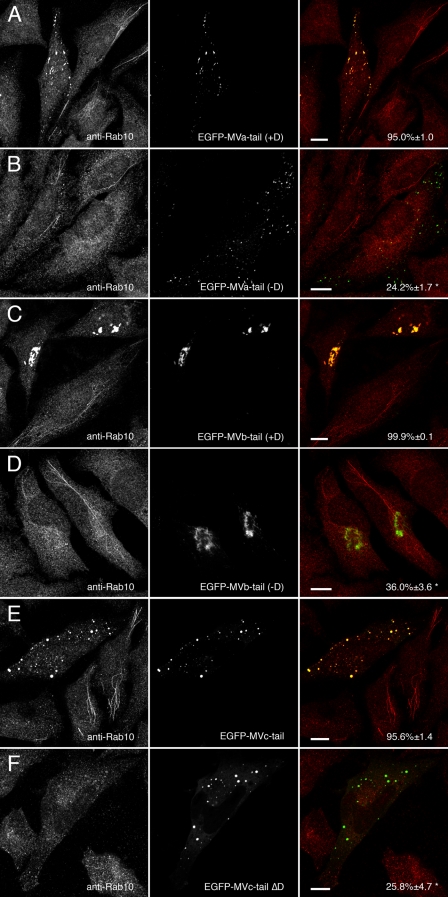
FIGURE 3.
Only myosin V tails expressing exon D alter endogenous Rab10 distribution. A, HeLa cells transfected with EGFP-myosin Va tail splice isoform containing exon D (EGFP-MVa-tail +D) and stained for Rab10. EFGP-myosin Va tail +D caused endogenous Rab10 to mislocalize to EGFP-labeled puncta. B, EGFP-myosin Va tail-brain splice isoform, which lacks exon D (EGFP-MVa-tail -D), also localized to disperse puncta but was unable to recruit endogenous Rab10. C and D, HeLa cells transfected with EGFP-myosin Vb tail expressing exon D (EGFP-MVb-tail +D) or lacking exon D (EGFP-MVb-tail -D) and stained for Rab10. Both splice variants of EGFP-myosin Vb tail localized to a perinuclear cisternum, but only myosin Vb tail expressing exon D caused Rab10 to mislocalize to the same cisternum. E and F, HeLa cells transfected with wild-type EGFP-myosin Vc tail, which contains an exon D-like domain (EGFP-MVc-tail) or a synthetic construct lacking exon D (EGFP-MVc-tail ΔD) and stained for Rab10. Similar to myosin Va and myosin Vb, myosin Vc tail required exon D to recruit Rab10. Scale bars in all panels represent 10 μm. Percent co-localization (±S.E.) are listed in the merged images on the right of each panel (n ≥ 10). *, statistically significant difference comparing +D and -D constructs (p < 0.001).