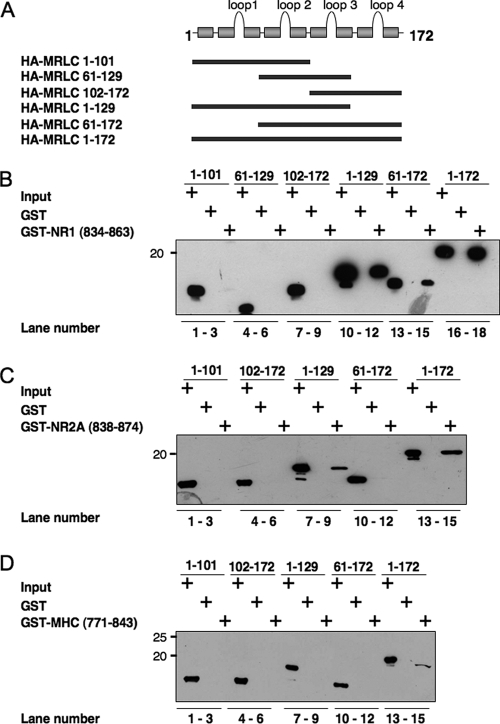
FIGURE 8.
The interaction of myosin RLC with NMDA receptor target sequences can be distinguished from RLC-heavy chain interactions. A, schematic representation of a series of hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged myosin RLC deletion mutants used in B-D. B, truncated recombinant myosin RLC-(1-129) is sufficient for NR1-(834-938) binding (compare lanes 12 and 18). C, interaction of myosin RLC with NR2A-(834-874) is qualitatively similar to that of NR1, inasmuch as myosin RLC-(1-129) is sufficient for NR2A binding (compare lanes 9 and 15). D, full-length myosin RLC is necessary for binding non-muscle myosin II-B heavy chain (MHC); all deletion mutants of myosin RLC failed to bind the neck region of the heavy chain MHC-(771-843). Three RLC target sequences, NR1, NR2A, and myosin heavy chain, fused to GST, were tested for their ability to bind full-length and mutant RLCs. GST fusion proteins, or GST alone, were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated at 4 °C with rotation overnight in the presence of 1 mm magnesium with either full-length (MRLC-(1-172)) or truncated light chains as follows: MRLC-(1-101), MRLC-(61-129), MRLC-(102-172), MRLC-(1-129), and MRLC-(61-172). Bound proteins were resolved by PAGE and blotted to nitrocellulose. Immune complexes were revealed by anti-T-7 antibody (Novagen). B-D are representative of three or four (NR2A) independent determinations.