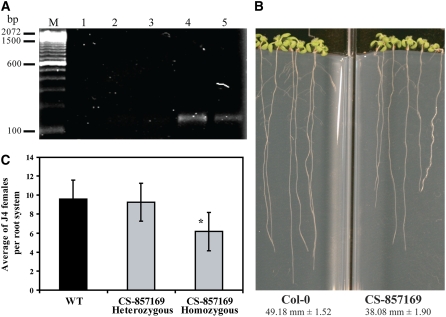
Figure 4.
The pme3 Knockout Mutant Is Altered in Root Length and Susceptibility to H. schachtii.
(A) PME3 mRNA accumulation in the pme3 mutant. PME3 mRNA level was determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR using gene-specific primers. The real-time RT-PCR products were resolved on syber safe-stained 2% agarose gel. No PCR products were detected after 40 cycles of amplification of cDNA from homozygous mutant plants (lanes 1 to 3), whereas specific amplifications were detected after amplification of cDNA from either heterozygous (lane 4) or wild-type (Col-0) plants (lane 5). Molecular weight marker is a 100 bp ladder (Invitrogen).
(B) The pme3 knockout mutant develops shorter roots than the wild-type (Col-0). Homozygous plants were planted on modified Knop's medium with the wild type (Col-0), and root lengths were measured 15 d after planting. Root length values are averages of at least 30 plants ± se. Differences between pme3 and the wild type were statistically significant as determined by unadjusted paired t tests (P < 0.01).
(C) The pme3 knockout mutant is less susceptible to H. schachtii than the wild type (Col-0). The pme3 knockout mutant (homozygous and heterozygous) and wild-type (Col-0) plants were planted on modified Knop's medium, and 2-week-old seedlings were inoculated with ∼250 surface-sterilized J2 H. schachtii. Two weeks after inoculation, the number of J4 female nematodes per root system was counted. Data are presented as the mean ± se. Mean values significantly different from that of the wild type as determined by unadjusted paired t tests (P < 0.05) are denoted by an asterisk. Identical results were obtained from at least four independent experiments.