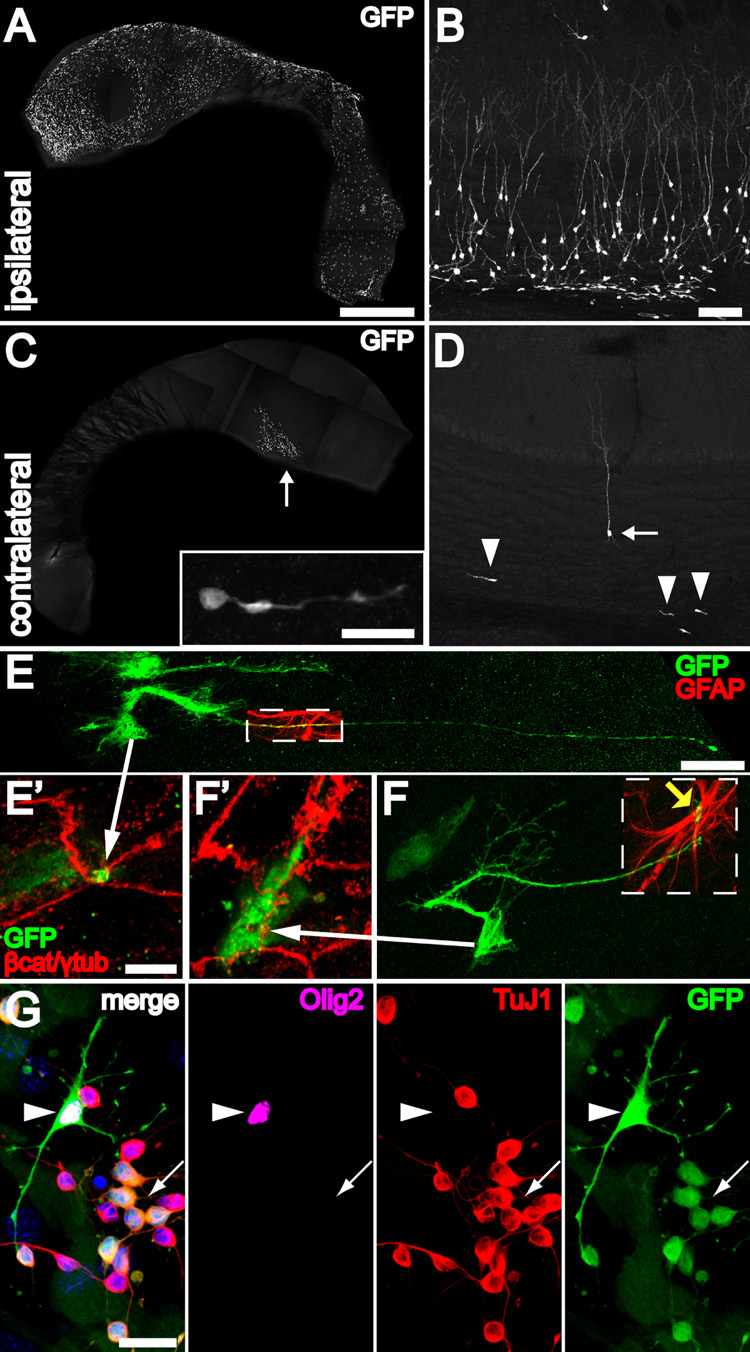
Figure 7. B1 cells with apical ventricular contact are neurogenic in vivo and differentiate into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in vitro.
(A) Injection of adeno-GFAPp:Cre into one LV of Z/EG mice results in many labeled ventricle-contacting B1 cells on the ipsilateral lateral wall. The wholemount images (A, C) were reconstructed from low power (1.3 mm × 1.3 mm) tiled confocal images. Scale bar = 1 mm (A, C)
(B) 30 days after injection, many labeled neurons and neuroblasts can be found in the ipsilateral olfactory bulb. Scale bar = 100 um (B, D).
(C) Virus that backfills the contralateral LV labels a few ventricle-contacting B1 cells on the contralateral side. Most of these labeled cells are close to the foramen of Monro (arrow). These labeled B1 cells give rise to neuroblasts (inset) in the contralateral SVZ, examined 30 days after injection. Inset: Scale bar = 20 um.
(D) The few labeled ventricle-contacting B1 cells on the contralateral side gave rise 30 days later to neuroblasts (arrowheads) and neurons (arrow) in the contralateral OB.
(E, F) B1 cells in the contralateral lateral wall have characteristic features of apical ventricular contact (arrows to E’, F’), GFAP expression (boxed regions), and a long basal process with endfeet on blood vessels (yellow arrow). Scale bar = 25 um.
(E’, F’) Confocal images of the ventricle-contacting apical surface of B1 cells in (E, F). Scale bar = 5 um.
(G) GFP-labeled B1 cells dissected from the contralateral wall could be passaged and differentiated in vitro into TuJ1+ neurons (arrow), Olig2+ oligodendrocytes (arrowhead), and adherent GFAP+ (not shown) astrocytes. Scale bar = 20 um.