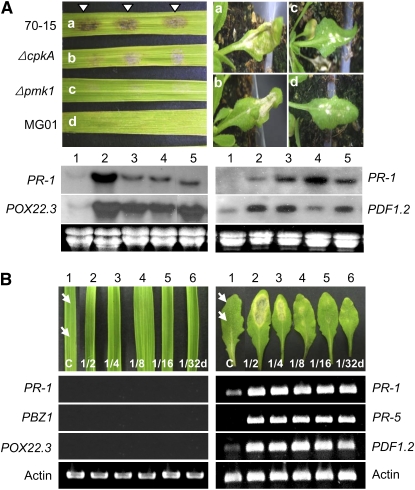
Figure 8.
Comparison of responses in rice and Arabidopsis to three M. oryzae mutants defective in infecting rice and M. oryzae fungal culture filtrates. A, Disease symptoms caused by 70-15 (a), ΔcpkA (b), Δpmk1 (c), and MG01 (d) at 48 h. Rice plants (cv Nakdongbyeo) were inoculated with three drops of a spore suspension (105 conidia mL−1), whereas Arabidopsis plants (ecotype Nd-0) were sprayed with the suspension. Levels of two genes in the infected leaves of each host (PR-1 and POX22.3 for rice and PR-1 and PDF1.2 for Arabidopsis) collected at 2 dpi were measured via northern hybridization: mock (lane 1), 70-15 (lane 2), ΔcpkA (lane 3), Δpmk1 (lane 4), and MG01 (lane 5). B, Comparison of the responses to a CF of KJ201 between rice and Arabidopsis. Two drops (10 μL each) of a concentrated CF of KJ201 and several dilutions (1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32) were dropped onto rice (cv Nakdongbyeo) and Col-0 leaves (indicated by arrows). As a control, leaves were treated with a mixture of distilled water and acetone (50:50, mock; lane 1). The leaves were then monitored for 3 d. At 3 dpi, RNA was extracted from individual leaves to check the level of expression of three genes by reverse transcription-PCR: PR-1, PBZ1, and POX22.3 for rice and PR-1, PR-5, and PDF1.2 for Arabidopsis.