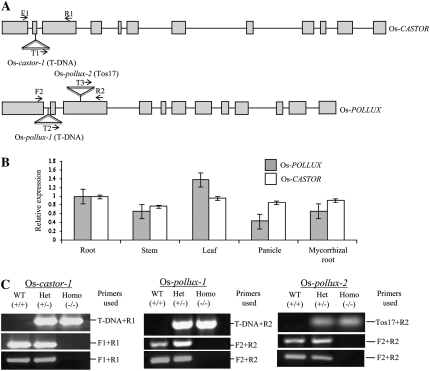
Figure 2.
Isolation and characterization of Tos17/T-DNA insertion mutants of Os-CASTOR and Os-POLLUX. A, Gene structures of Os-CASTOR and Os-POLLUX and the Tos17/T-DNA insertion sites. The exons and introns are indicated by boxes and lines, respectively. Insertion sites of Tos17/T-DNA are indicated. B, Os-CASTOR and Os-POLLUX expression levels in roots, stems, leaves, panicles, and mycorrhizal roots. Relative transcript abundance was determined by qRT-PCR and normalized against Os-ubiquitin1. Error bars represent sd values from three independent biological replications. C, Identification of homozygous (–/–) insertion mutants by PCR. Top, Identification of positive insertion plants (+/– or –/–) by PCR using a pair of Tos17/T-DNA- and gene-specific primers. Middle, PCR analysis to distinguish between homozygous (–/–) and heterozygous (+/–) mutant plants using a primer pair flanking the Tos17/T-DNA insertion site that allowed the amplification of only the wild-type (WT) allele under given PCR conditions. Bottom, RT-PCR analysis of Os-CASTOR and Os-POLLUX expression in the wild-type and mutant plants. The primer positions are indicated in A.