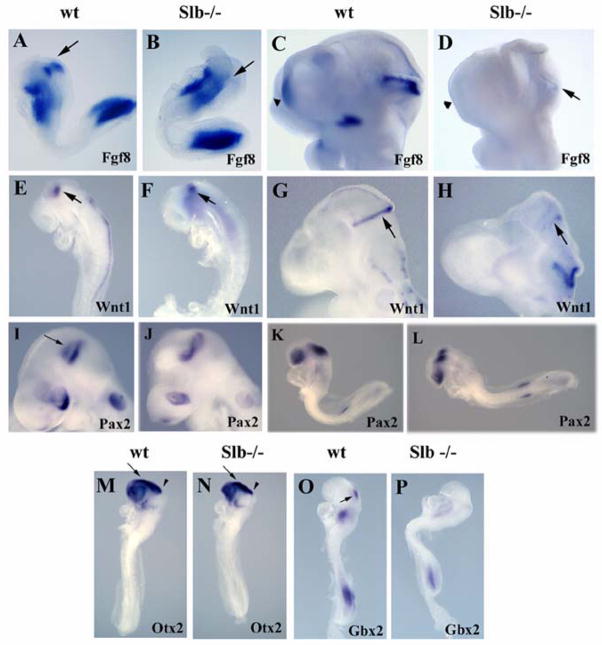
Figure 5. Defects in isthmic organizer formation and forebrain development.
(A, B) At E8.3, expression of Fgf8 at the MHB boundary (arrow) is severely downregulated in Slb mutant embryos (B) as compared to the wild type (A). (C, D) AtE9.5, Fgf8 is present at the MHB boundary of the wild type embryo (C), butis barely detectable in the Slb mutant (arrow in D). Fgf8 transcripts are normally expressed in the commissural plate (CP) of the wild type embryo, but are not found in the forebrain of the mutant (arrowheads in C and D). (E, F) At E8.5, Wnt1 expression at the MHB boundary (arrow) of the Slb mutant embryo (F) is comparable to that of the wild typeembryo (E), but missing in the dorsal neural tube. (G, H) At E9.5 the Wnt1 expression at theMHB boundary is maintained in the wild type (arrow in G), but is virtually lost in the Slb mutant embryo (H). (I, J) The most anterior Pax2 expression domain atthe MHB boundary (arrow in I) is absent in the Slb mutantembryo (J). (K, L) Pax2 expression is not reduced in the mutant at E8.5 (L) compared to the wild type embryo (K). (M, N) Otx2 expression in the forebrain (arrow) and midbrain (arrowhead) regions of E8.5 Slb mutant embryo (N) is comparable to that of the wild type embryo (M). (O, P) At E8.5, Gbx2 is severely affected in the Slb mutant (P) compared to the wild type (arrow in O).