Figure 1.
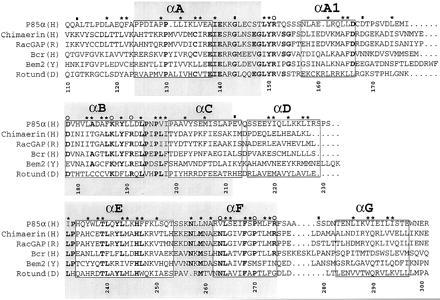
A sequence alignment of a subset of BRC-homology (BH) domains. A larger alignment, comprising 22 sequences, was used to evaluate the degree of sequence conservation at each position. The sequences used, with their database accession number for each sequence listed last in parentheses, are reported (B, bovine; CE, Caenorhabditis elegans; D, Drosophila melanogaster; H, human; M, mouse; R, rat; Y, Saccharomyces cerevisiae): (H) breakpoint cluster region (Bcr) (P11274); (H) ABR (U01147); (M) 3BP1 (X87671); (R) p122 (D31962); (R) p190 (M94721); (H) C1 (X78817); (Y) Bem2 (P39960); (Y) Bem3 (P32873); (R) β-chimaerin (Q03070); (H) IT5P (P32019); (Y) RGA1 (P39083); (D) Rotund (P40809); (M) p85α (P26450); (H) p85α ((P27986); (B) p85α (P23727); (B) p85β (P23726); (H) n-chimaerin (P15882); (R) n-chimaerin (P30337); (H) OCRL (Q01968); (Y) YB9G (P38339); (H) RhoGAP (Z23024); (CE) CeGAP (U02289). Residues that were conserved in at least 14 sequences out of 22 are shown in bold type. Asterisks above columns indicate residues whose side chains are part of the hydrophobic core of the molecule. Open circles identify residues that are part of the proposed ligand-binding site. Filled rectangles indicate residues lying at intron–exon boundaries in the mouse p85α gene (12). Each helical fragment boxed. The N- and C-terminal residues of each helix were defined as the first and last residues whose main chain carbonyl and amide groups, respectively, were involved in an intrahelical hydrogen bond. The gray boxes identify three blocks of conservation discussed in the text. Numbering corresponds to full-length human p85α. The alignment was generated with the pileup program (GCG package). The image was created using the programs Adobe illustrator and Adobe photoshop (Adobe Systems, Mountain View, CA).
