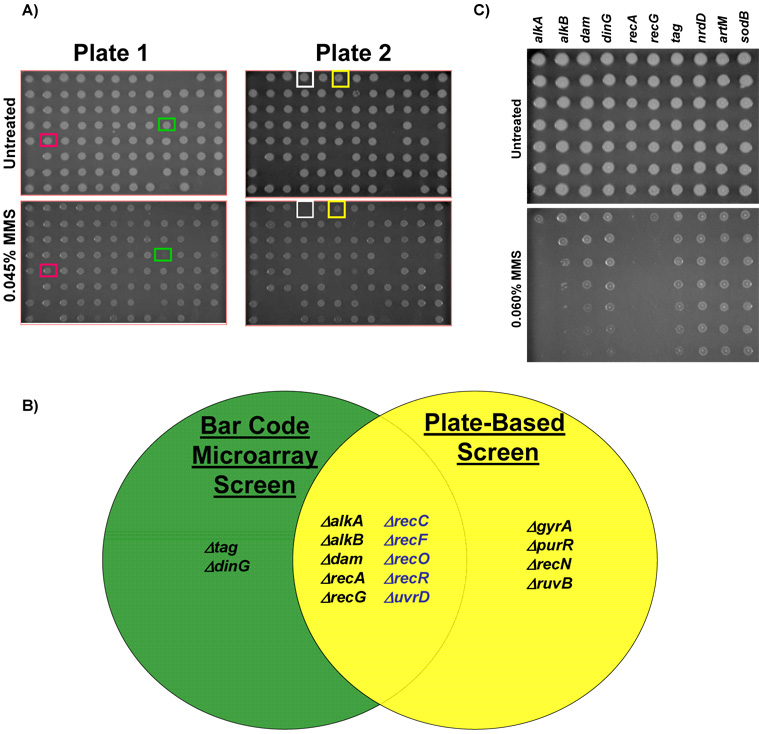
Figure 4. Classification of MMS Sensitive Gene Deletion Mutants Using Plate-based Assays.
(A) Robotic spotting of bar-coded mutants on increasing concentrations of MMS. The plate key can be found in supplementary table S3 with rows labelled A to H and columns 1 to 12. Representative MMS sensitive mutants; ΔgyrA (green box) and ΔalkB (white box) as well as well two no phenotype mutants Δtag (red box) and ΔdinG (yellow box), which surprisingly exhibited no phenotype in this assay. (B) A Venn diagram illustrating the overlap of results from plate and microarray based screens. Mutants displayed in blue represent MMS sensitive mutants identified with a relaxed criterion [log2 (untreated / MMS-treated) ≥ 1-fold] in the microarray screen. (C) Overnight cultures of each microarray classified MMS sensitive mutant were 10-fold serially diluted and 5 ul aliquots were spotted on LB-chloramphenicol plates (−/+ 0.015% MMS). Plates were incubated for 16 hours at 37°C and then digitally imaged. Gene delet ion mutants classified as MMS sensitive on plates were identified using the three wild-type surrogates (ΔnrdD, ΔartM, ΔsodB) and verified against wild-type BW25113 (not shown). Gene deletion strains classified as MMS-sensitive on these plates were ΔalkA, ΔalkB, Δdam, ΔrecA, and ΔrecG.