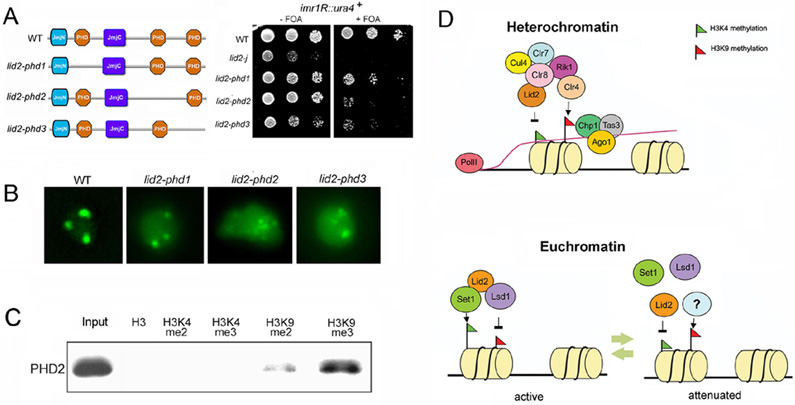
Figure 7. PHD domains are important for Lid2’s function.
A) PHD domains affect heterochromatin silencing as shown by a silencing assay. Left panel shows the schematic representation of Lid2 and its PHD domain deletion mutants. Strains containing the ura4+ marker at centromere imr region as indicated were plated by serial dilution on the FOA media.
B) PHD2 and PHD3 domains affect GFP-Swi6 distribution in the nucleus. Aberrant GFP-Swi6 patterns were observed in lid2-phd2 and lid2-phd3, similar to lid2-j, suggesting that these PHD domains may also involve in euchromatin assembly.
C) PHD2 domain preferentially binds to H3K9me3 methylated peptide. PHD domains tagged with TAP-tag were purified and incubated with biotinylated histone peptides methylated at different lysine residues, as indicated. Bound proteins are then eluted from the avidin beads, and resolved by SDS–PAGE followed by Western blotting using antibody against TAP-tag.
D) Model for Lid2 function: Lid2 demethylates heterochromatic H3K4me3 and also mediates H3K9 methylation by Clr4 through interaction with Clr8-Rik1 complex (upper panel). This stabilizes the RITS association with chromatin which in turn recruits RDRC complex to synthesize the double strand RNA for dicer. At euchromatin (lower panel), Lid2 recruits Set1 and Lsd1 to maintain H3K4 methylation and at the same time removes H3K9 marks in actively transcribing genes. During the attenuation phase of transcription , Lid2 H3K4 demethylase activity could be triggered to reduce the H3K4 methylation level.