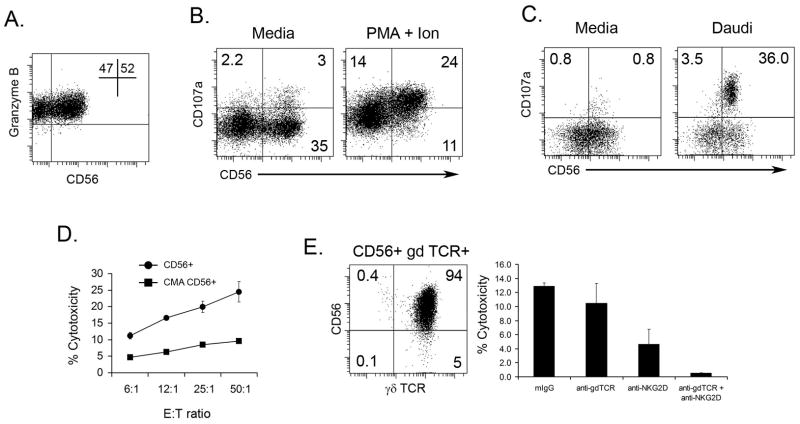
Figure 5. Expression of degranulation marker (CD107a) is increased in CD56+ γδ T cells after stimulation.
γδ T cells were generated by expanding PBMC (see Materials and Methods). A. Cells were stained with anti-CD56 and anti-Granzyme B and analyzed by flow cytometry. B. Expanded γδ T cells were cultured with either media or PMA and Ionomycin in the presence of CD107a-FITC mAB for 4 hours (see Materials and Methods). The cells were then stained for anti-CD3, anti-γδTCR, and anti-CD56 and analyzed by flow cytometry. C. Expanded γδ T cells were separated for CD56+ and CD56− populations using magnetic beads. The populations were then cultured with media or Daudi cells in the presence of CD107a-FITC mAB anti-CD107a. After 15 hours, the cells were stained with anti-CD3, anti-γδTCR, and anti-CD56 and analyzed by flow cytometry. A representative dot blot from one of three experiments is shown. D. Expanded γδ T cells were incubated with CMA during the standard 4 h 51Cr-release assay against TU159 SCCHN cell line. One of three independent experiments is shown. E. The cytotoxic activity against TU159 of highly purified CD56+ γδ T cells (dot plot) was measured in standard 4 h 51Cr-release assay. Blocking anti-γδ TCR antibodies were added into the wells containing CD56+ γδ T cell effectors and TU159 HNSCC cell line for the duration of the cytotoxicity test. Cytotoxicity is shown for 12:1 Effector:Target ratio.