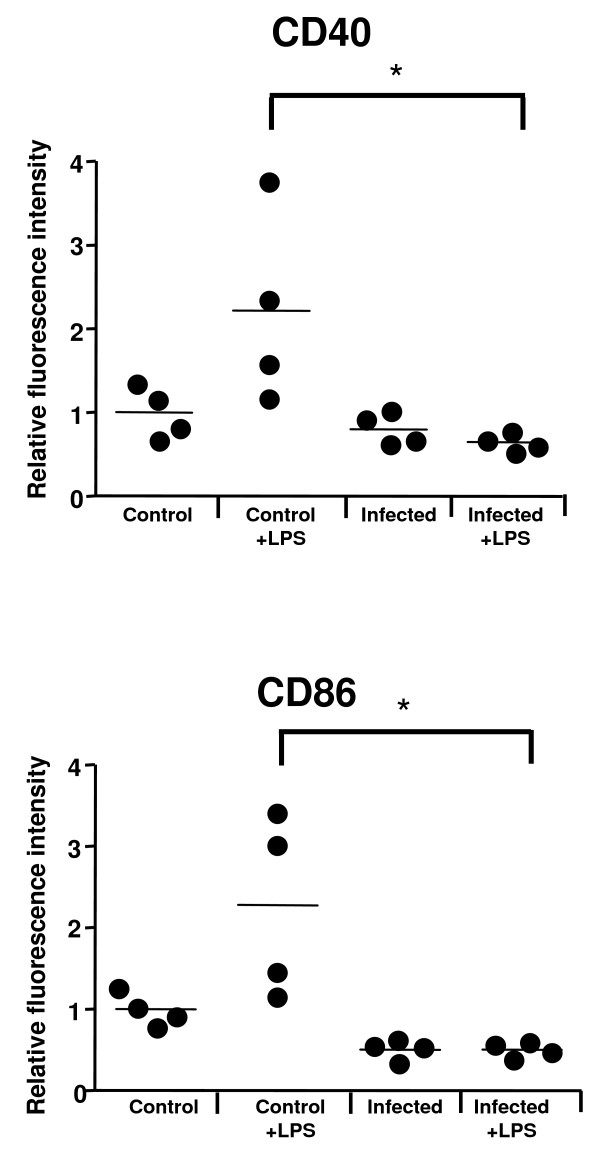
Figure 1.
P. yoelii infection inhibits the in vivo maturation of CD11c+ splenocytes. SW mice were infected or not with 106 P. yoelii-infected erythrocytes. At day 10 post infection, CD11c+ splenocytes were analysed via flow cytometry for their surface expression of co-stimulatory molecules CD40 and CD86. When indicated, 25 μg/mouse of LPS was injected intravenously 24 h prior to spleen harvest. Results are expressed as relative fluorescent intensity for the gated CD11c+ cells of each mouse compared with the average of gated CD11c+ cells from uninfected, unstimulated mice. Each symbol is representative of one mouse and each group contains at least 3 mice. Bars represent mean value of each group of mice. Differences in surface expression were considered significant when p < 0.05. * represents significant differences in surface expression when compared to LPS treated uninfected mice.