Figure 7.
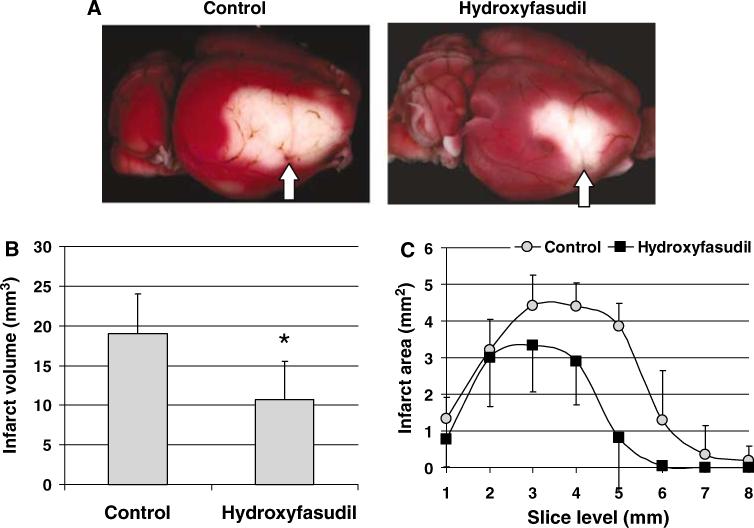
Hydroxyfasudil improved tissue outcome in wild-type mice. (A) Topical 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride stained brains from representative control and hydroxyfasudil-treated (10 mg/kg, i.p., 1 h before dMCAO) mice demonstrating the infarct in the dorsolateral cortex. Arrow indicates the site of dMCAO using a microsurgical clip (see Methods). (B) Hydroxyfasudil reduced infarct volume by 45% when measured 48 h after 1 h transient dMCAO (*P < 0.05 versus control, t-test, n = 5 in each group). Infarct volume was calculated by integrating the infarct area in 1 mm thick coronal slices; because of the relatively small volume of infarct, only direct infarct volume was determined. (C) Graph showing the infarct area at each coronal slice level. Hydroxyfasudil reduced the infarct size mainly in the posterior cortical regions. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of the mean.
