Fig. 3.
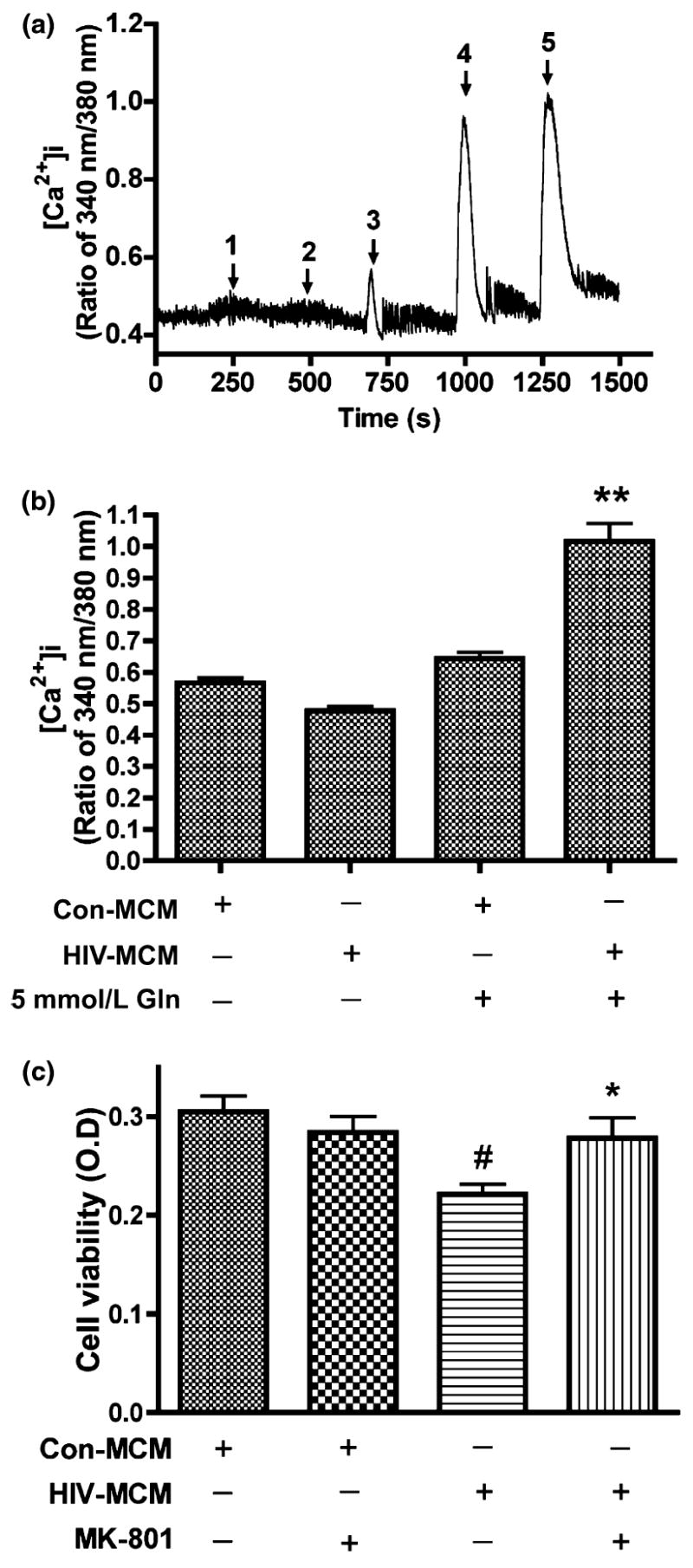
HIV-MCM mediates neurotoxicity through over-stimulation of NMDA Receptors and NMDAR antagonist (MK801) blocks HIV-MCM-mediated neurotoxicity. Rat cortical neurons were loaded with Fura-2 and monitored for calcium influx by micro-fluorescent imaging. Filtered control MCM and HIV-1 MCM (including Glutamine free or 5 mmol/L glutamine) were tested to see the responses of NMDA receptor (a), 1: Con Gln free MCM; 2: HIV Gln free MCM; 3: Con 5 mmol/L Gln MCM; 4: HIV 5 mmol/L Gln MCM; 5: 100 μmol/L Glu. Panel B expressed as mean ± SD. Data represent five independent experiments. **denotes p < 0.001 in comparison to control MCM with 5 mmol/L glutamine and HIV-MCM without 5 mmol/L glutamine. (c) NMDA receptor antagonist MK801 blocks the neurotoxic effect of HIV-1 infected MCM. Rat cortical neurons were pre-treated with 10 μmol/L MK801 for 15 min before MCM treatment. HIV-MCM induced significant neuronal death and this kind of neurotoxic effect was blocked by MK801. The results are expressed as mean ± SD. #denotes p < 0.05 compared with related control MCM; *denotes p < 0.01 in comparison with HIV-MCM.
