Figure 2. A selection of example scatterplots that demonstrate experimental condition-dependent correlation between metabolites and related genes, motivating the use of a Bayesian algorithm.
Metabolite and gene transcript concentration changes are represented as 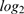 ratios of measurements from starved cells to measurements from unstarved cells. The responses observed under carbon starvation (light gray circles, “Carbon” in legend) are labeled distinctly from the responses under nitrogen starvation (dark gray triangles, “Nitrogen” in legend), but are plotted on the same axes. Solid light gray and dark gray lines are linear best-fits for the responses observed under carbon and nitrogen starvation, respectively; the dashed line is a linear best-fit curve for all data. (A–E) Scatterplots of metabolites from the glycolysis and pentose-phosphate pathway metabolic class versus related genes show an inverse relationship under carbon starvation, but a positive correlation under nitrogen starvation. The dashed line shows that this relationship would be obscured by computing correlation across all data points. ILV2 catalyzes the first step of isoleucine and valine biosynthesis from pyruvate; ARO3 catalyzes the first step in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis from PEP and erythrose-4-phosphate; ALD6, which also plays a key role in redox metabolism, is involved in the creation of cytosolic acetyl-CoA from pyruvate; GLK1 phosphorylates glucose to glucose-6-phosphate; and PGM2 catalyzes the interconversion of glucose-1-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate. (F–H) Scatterplots of metabolites from the amino acid metabolic class versus related genes, in contrast, show positive correlation in both carbon and nitrogen starvation. Even in this case, however, computing correlation across both conditions can lead to an underestimation of the extent of the relationship (e.g., (H) threonine vs. THR4, where although
ratios of measurements from starved cells to measurements from unstarved cells. The responses observed under carbon starvation (light gray circles, “Carbon” in legend) are labeled distinctly from the responses under nitrogen starvation (dark gray triangles, “Nitrogen” in legend), but are plotted on the same axes. Solid light gray and dark gray lines are linear best-fits for the responses observed under carbon and nitrogen starvation, respectively; the dashed line is a linear best-fit curve for all data. (A–E) Scatterplots of metabolites from the glycolysis and pentose-phosphate pathway metabolic class versus related genes show an inverse relationship under carbon starvation, but a positive correlation under nitrogen starvation. The dashed line shows that this relationship would be obscured by computing correlation across all data points. ILV2 catalyzes the first step of isoleucine and valine biosynthesis from pyruvate; ARO3 catalyzes the first step in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis from PEP and erythrose-4-phosphate; ALD6, which also plays a key role in redox metabolism, is involved in the creation of cytosolic acetyl-CoA from pyruvate; GLK1 phosphorylates glucose to glucose-6-phosphate; and PGM2 catalyzes the interconversion of glucose-1-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate. (F–H) Scatterplots of metabolites from the amino acid metabolic class versus related genes, in contrast, show positive correlation in both carbon and nitrogen starvation. Even in this case, however, computing correlation across both conditions can lead to an underestimation of the extent of the relationship (e.g., (H) threonine vs. THR4, where although  and
and  ,
,  ). HTS1 charges (i.e. aminoacylates) the histidinyl-tRNA; MET6 catalyzes the formation of methionine from homocysteine; and THR4 converts phosphohomoserine to threonine.
). HTS1 charges (i.e. aminoacylates) the histidinyl-tRNA; MET6 catalyzes the formation of methionine from homocysteine; and THR4 converts phosphohomoserine to threonine.

