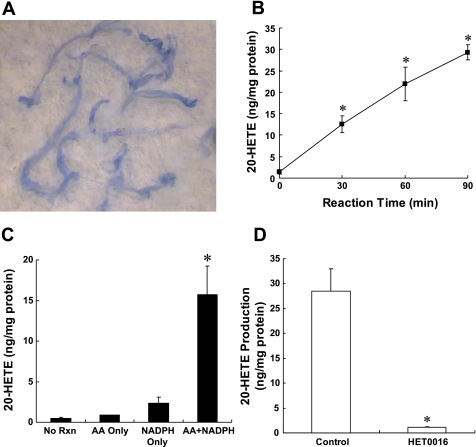
Fig. 1.
A: typical appearance of the cerebral arteries isolated by an Evans blue sieving procedure. The vessels are displayed on the background of a filter paper and are intact and relatively free of brain parachymal tissue. B: levels of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) measured in cerebral arteries incubated with 40 uM arachidonic acid (AA) and 1 mM NADPH at 37°C for 0, 30, 60, and 90 min. Effect of addition of AA and NAPDH on the production of 20-HETE production in cerebral arteries is presented in C. Vessels were incubated for 90 min at 37°C in the presence of 40 μM AA alone, 1 mM NADPH in the absence of added substrate, or both NADPH and substrate. No reaction (RXN) corresponds to control levels of 20-HETE that were measured in vessels that were placed in cold incubation solution and then homogenized and extracted with being incubated. D: effect of 1 μmol/l N-hydroxy-N'-(4-butyl-2-methylphenyl)-formamidine (HET0016) on 20-HETE production in cerebral arteries. Mean values ± SE from at least 3 separate incubations of vessels prepared from different animals are presented per time point. *Significant difference from the corresponding control value.