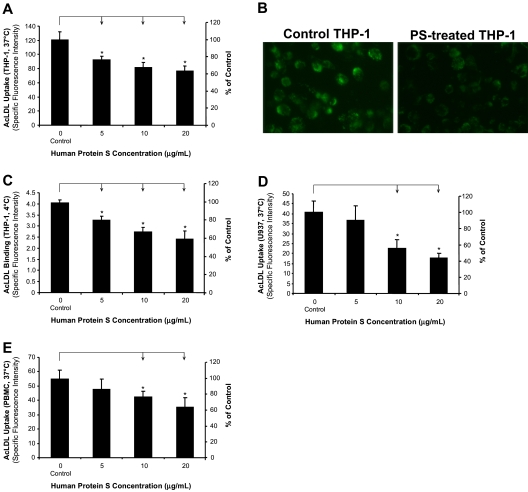
Figure 1.
Inhibitory effects of human protein S on AcLDL uptake and binding by human monocyte–derived macrophages. (A,B) AcLDL uptake in THP-1 macrophages. The cells were treated with protein S for 24 hours, followed by incubation with 5 μg/mL Alexa Fluor 488–AcLDL in the presence or absence of 250 μg/mL AcLDL for 3 hours at 37°C. The fluorescence intensity of cells was measured with a fluorescence microplate reader and photographed with a fluorescent microscope (Olympus IX51 with SPOT camera; total magnification ×200). (C) AcLDL binding to THP-1 macrophages. The cells were treated with protein S for 24 hours, followed by incubation with 5 μg/mL Alexa Fluor 488–AcLDL in the presence or absence of 250 μg/mL AcLDL for 30 minutes at 4°C. (D) AcLDL uptake in U937 macrophages. The cells were treated with protein S for 24 hours, followed by incubation with 5 μg/mL Alexa Fluor 488–AcLDL in the presence or absence of 250 μg/mL AcLDL for 3 hours at 37°C. (E) AcLDL uptake in human PBMC–derived macrophages. The cells were treated with protein S for 24 hours, followed by incubation with 5 μg/mL Alexa Fluor 488–AcLDL in the presence or absence of 250 μg/mL AcLDL for 3 hours at 37°C. Columns and bars denote the mean and SD of 3 experiments. *P < .05 versus untreated controls.