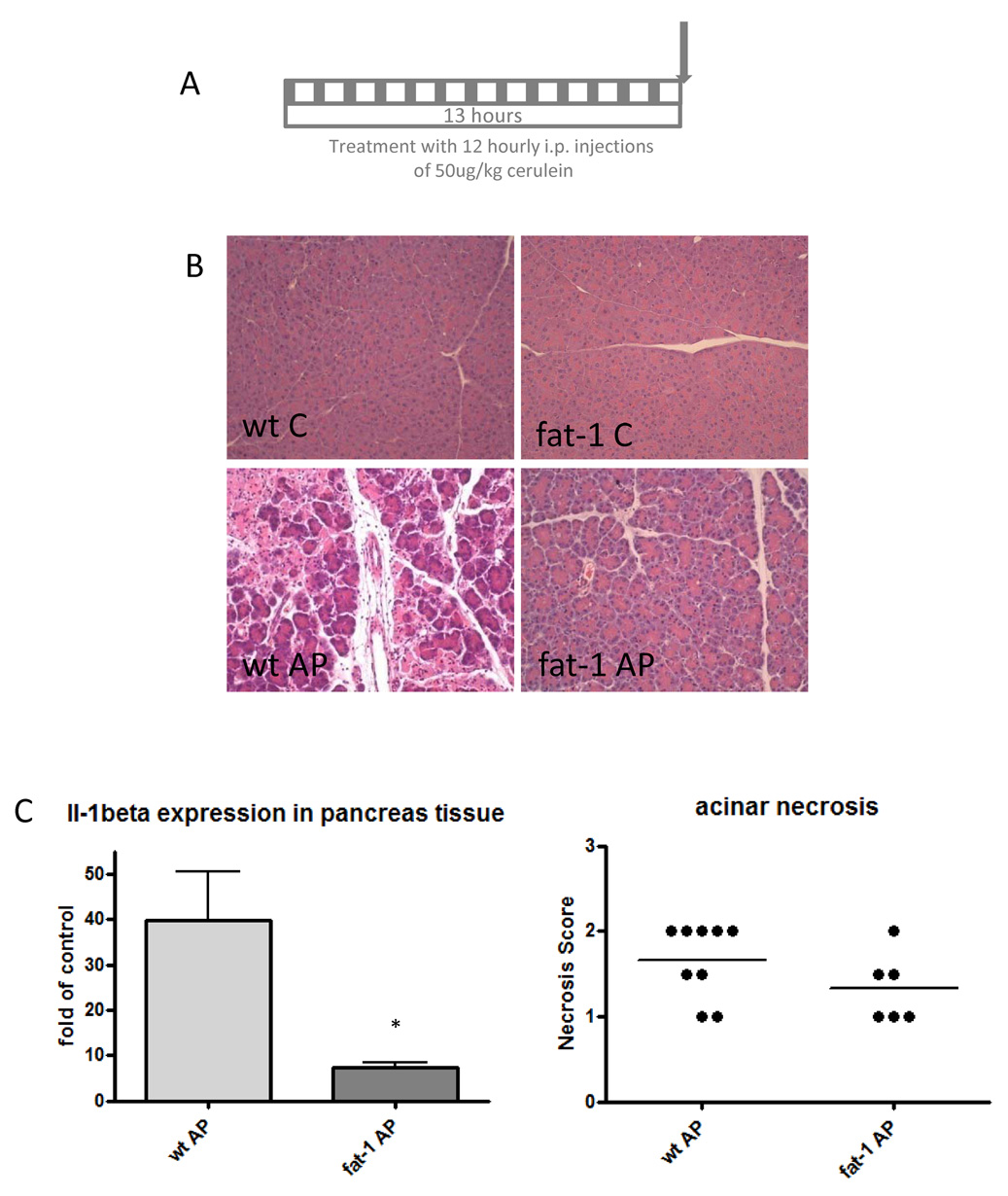
Figure 1. Acute pancreatitis in fat-1 and wild-type mice.
A. Acute pancreatitis was induced by 12 hourly intraperitoneal injections of cerulein.
B. Fat-1 treated mice are less susceptible to injury caused by the cerulein-induced pancreatitis. As compared to saline-injected wild-type (upper left panel) and fat-1 (upper right panel) control animals, the pancreas of wild-type mice injected with cerulein show acinar cell destruction and necrosis (lower left). These histological signs of acute pancreatitis are reduced in fat-1 mice treated with cerulein (lower right). Hematoxylin-Eosin stains (200×) are shown for the different groups.
C. Expression of IL-1β m-RNA, measured by quantitative real time RT-PCR, in mice with acute pancreatitis, n=3 for both groups. *p<0.05 versus wild-type mice with acute pancreatitis.
D. Pancreatic necrosis score in mice with acute pancreatitis. Differences were not significant.