FIGURE 4. Trans-phosphorylation of SFK.
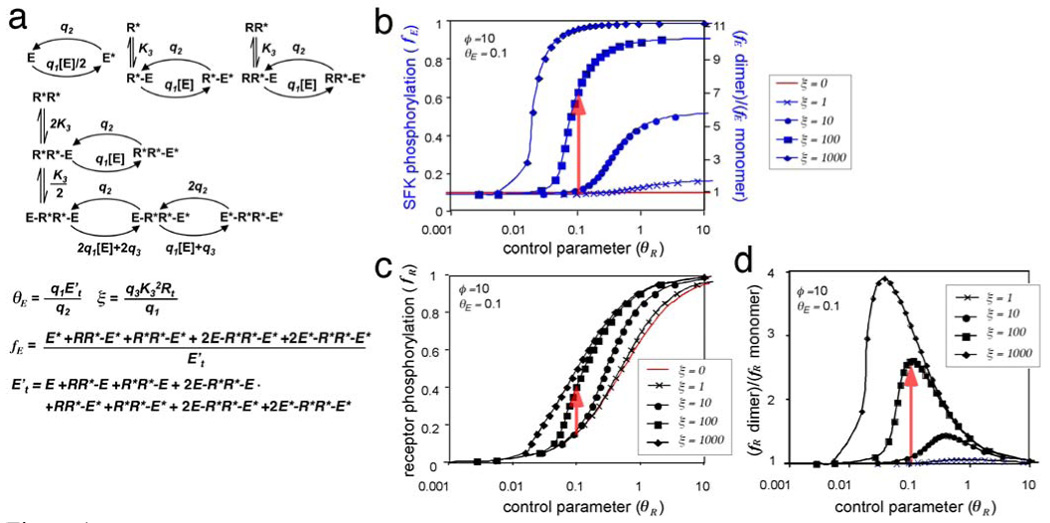
(a) Reactions and equations describing the intermolecular phosphorylation of E. Phosphorylation of E, alone or complexed with various forms of R*, occurs with bi-molecular rate constant q1, and dephosphorylation occurs with pseudo-first order rate constant q2. q4 represents SFK trans-phosphorylation within a E-R*R*-E complex. These reactions are solved in Appendix 3.
(b) Fractional SFK phosphorylation (fE) as a function of the control parameter for receptor phosphorylation (θR), for particular values of the phosphorylation-induced increase in SFK activity (ϕ) and the control parameter for SFK phosphorylation (θE). The control (red) is for monomeric receptors. Blue lines show results for dimeric receptors with various values of the SFK trans-phosphorylation parameter (ξ). Dimerization does not change any parameter except σ, which increases fE (red arrow).
(c) Fractional receptor phosphorylation. Same parameters as in (b).
(d) Relative increase in receptor phosphorylation due to dimerization. These graphs were constructed by interpolation of the data in (c).
