Fig. 1.
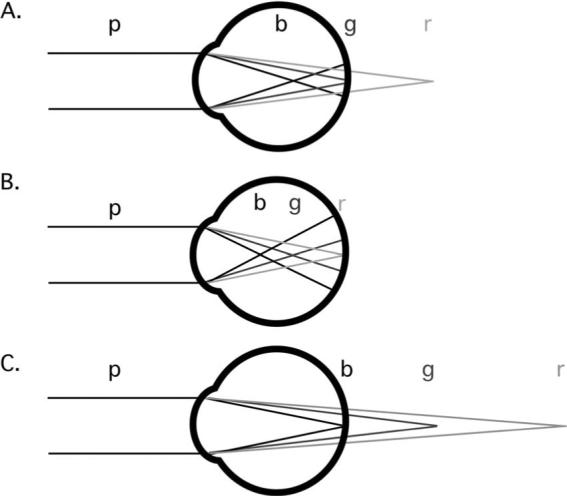
Schematic illustration of longitudinal chromatic aberration (LCA) and the effects of myopic and hyperopic defocus. Polychromatic light (p) reaches the eye and is dispersed into its component wavelengths. The power of the eye is greater for short (b) than the middle (g) and long (r) wavelengths. A. The middle (g) wavelengths are focused at the retina. B. An overpowered, myopic eye with the long (r) wavelengths in best focus. C. an underpowered, hyperopic eye with short (b) wavelengths in best focus.
