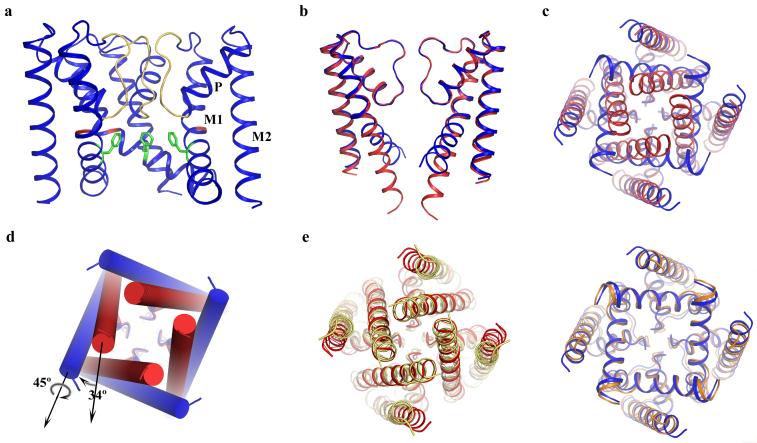
Figure 1.
Structure of NaKNΔ19 in an open conformation. (a) Overall structure of NaKNΔ19 with the front subunit removed for clarity. Selectivity filter residues, Gly87 and Phe92 are colored yellow, red and green, respectively. M1=outer helix, M2=inner helix, and P=pore helix b) Superimposition of the structures of NaKNΔ19 (blue) and NaK (red, PDB code 2AHY) with its M0 helix removed, viewed from the plane of the membrane with proximal and distal subunits removed and c) from the intracellular side. d) Conformational change of NaK inner helices from the closed (red cylinder) to open state (blue cylinder) involves a 34° bending and a 45° twisting around the helical axis. e) Comparison of NaK with KcsA (left) and MthK (right). Superimposition of the closed NaK structure (red, PDB code 2AHY) with KcsA (yellow, PDB code 1K4C) viewed from the intracellular side along 4-fold axis and the equivalent superimposition of the open NaKNΔ19 structure (blue) with the MthK pore (orange, PDB code1LNQ) are shown.