Figure 1.
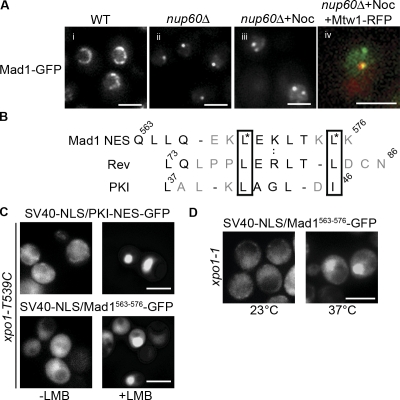
Mad1p contains a functional Xpo1p-dependent NES. (A) Mad1-GFP was visualized by fluorescence microscopy in WT (Y3028, i) or nup60Δ cells (Y3040, ii and iii; Y3057, iv). Mad1-GFP intranuclear Mlp1p/Mlp2p foci in the absence of Nup60p (ii). Treatment of nup60Δ cells with nocodazole induces recruitment of Mad1-GFP to kinetochores (iii) as conferred by colocalization with Mtw1-RFP (iv). (B) An alignment of the predicted NES in Mad1p with the NESs of HIV Rev and rabbit PKI is shown. Residues required for NES function in HIV Rev and PKI are boxed together with leucine residues in the Mad1p NES (asterisks). (C) Plasmids encoding SV40-NLS/PKI-NES-GFP and SV40-NLS/MAD1563–576-GFP3 were introduced into a strain expressing xpo1-T539C (Y3105 + pKW711). The localization of these reporters was examined by fluorescence microscopy before or 30 min after the addition of LMB. (D) SV40-NLS/MAD1563–576-GFP3 was introduced into the xpo1-1 Ts strain (Y3105 + pKW457) and observed at the permissive (23°C) or restrictive temperature (30 min at 37°C). Bars: (A) 2 μm; (C and D) 5 μm.